- How do I add ACL permissions in Linux?
- Where are ACL permissions stored?
- What are ACLs in Linux?
- How do I know if my ACL is enabled Linux?
- What is difference between ACL and chmod?
- How do I turn off ACL permissions?
- What is ACL authentication?
- What is ACL permission?
- Is an ACL a firewall?
- What is default ACL Linux?
- Why we use ACL in networking?
How do I add ACL permissions in Linux?
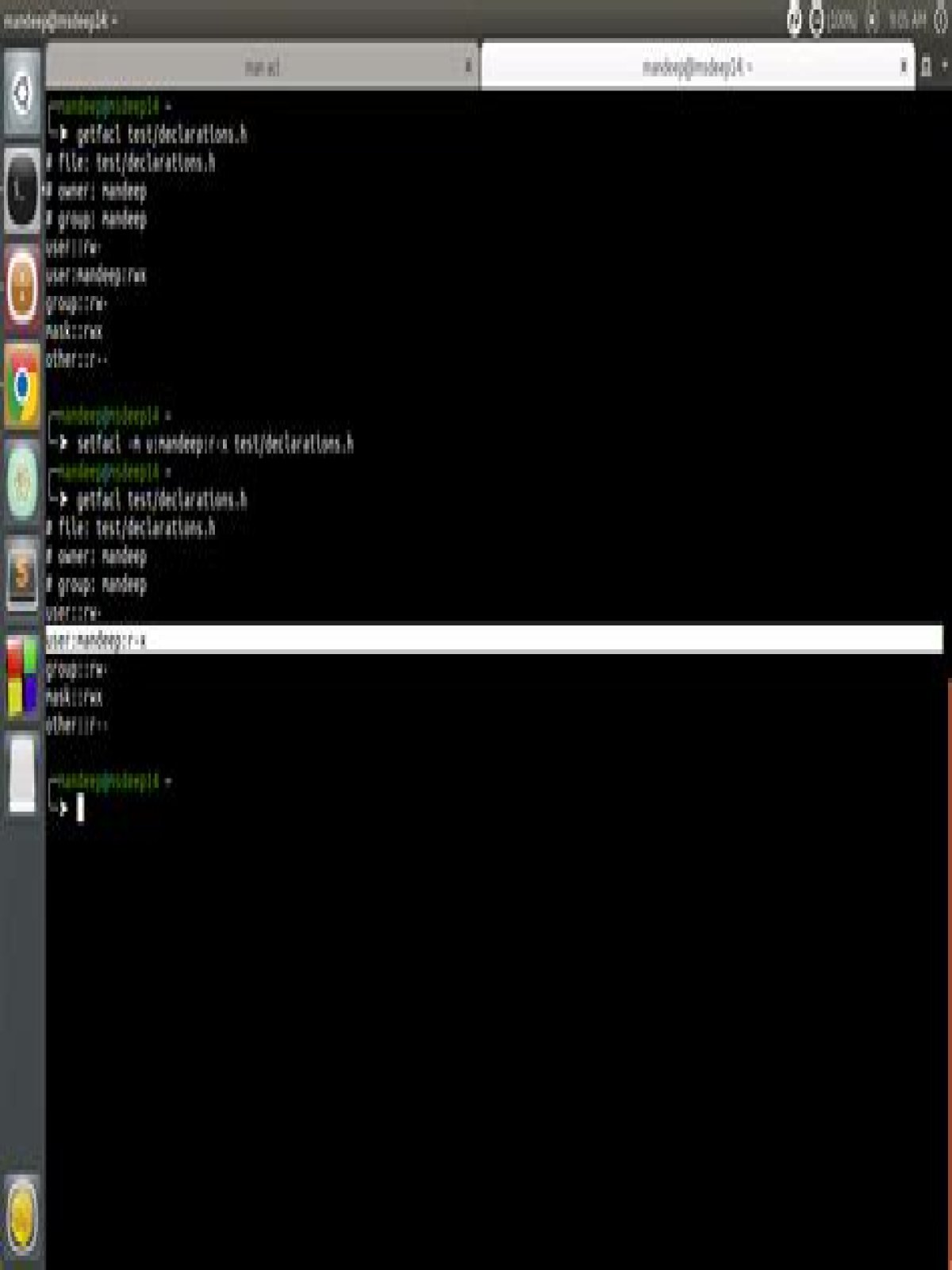
setfacl and getfacl are used for setting up ACL and showing ACL respectively. Observe the difference between output of getfacl command before and after setting up ACL permissions using setfacl command. There is one extra line added for user mandeep which is highlighted in image above.
Where are ACL permissions stored?
3 Answers. The exact details may depend on the filesystem, but conceptually, yes, the ACLs are metadata stored in the file inodes just like traditional permissions, dates, etc. Since the size of ACLs can vary, they may end up being stored in separate blocks.
What are ACLs in Linux?
This type of situation is what Linux Access Control Lists (ACLs) were intended to resolve. ACLs allow us to apply a more specific set of permissions to a file or directory without (necessarily) changing the base ownership and permissions. They let us “tack on” access for other users or groups.
How do I know if my ACL is enabled Linux?
You can check if your filesystems have acl as part of the defaults by using the tune2fs command. As you can see on my test system the default mount options contain acl, in this case my filesystem will support acl’s even if I don’t specify it during the mount process.
What is difference between ACL and chmod?
Posix permissions only allows an owner, owning group and “everyone” permission while ACL allows multiple “owning” users and group. ACL also allows setting default permissions for new files in a folder. You can add more permission management on top of both with apparmor or selinux for stricter control.
How do I turn off ACL permissions?
So in order to remove ACLs just run setfacl -b -R on the directory, and chmod g=rwx afterwards. (Fixing group permissions might be needed, because currently your changes actually went to changing the ACL ‘mask’ instead.)
What is ACL authentication?
In computer security, an access-control list (ACL) is a list of permissions associated with a system resource (object). An ACL specifies which users or system processes are granted access to objects, as well as what operations are allowed on given objects.
What is ACL permission?
An access control list (ACL) contains rules that grant or deny access to certain digital environments. … Filesystem ACLs tell operating systems which users can access the system, and what privileges the users are allowed. Networking ACLs━filter access to the network.
Is an ACL a firewall?
An ACL is the same as a Stateless Firewall, which only restricts, blocks, or allows the packets that are flowing from source to destination. … ACLs are common in routers or firewalls, but they can also configure them in any device that runs in the network, from hosts, network devices, servers, etc.
What is default ACL Linux?
A Directory with a Default ACL. Directories can be equipped with a special kind of ACL — a default ACL. The default ACL defines the access permissions all objects under this directory inherit when they are created. A default ACL affects subdirectories as well as files.
Why we use ACL in networking?
Access control lists (ACLs) perform packet filtering to control the flow of packets through a network. Packet filtering can restrict the access of users and devices to a network, providing a measure of security. Access lists can save network resources by reducing traffic.