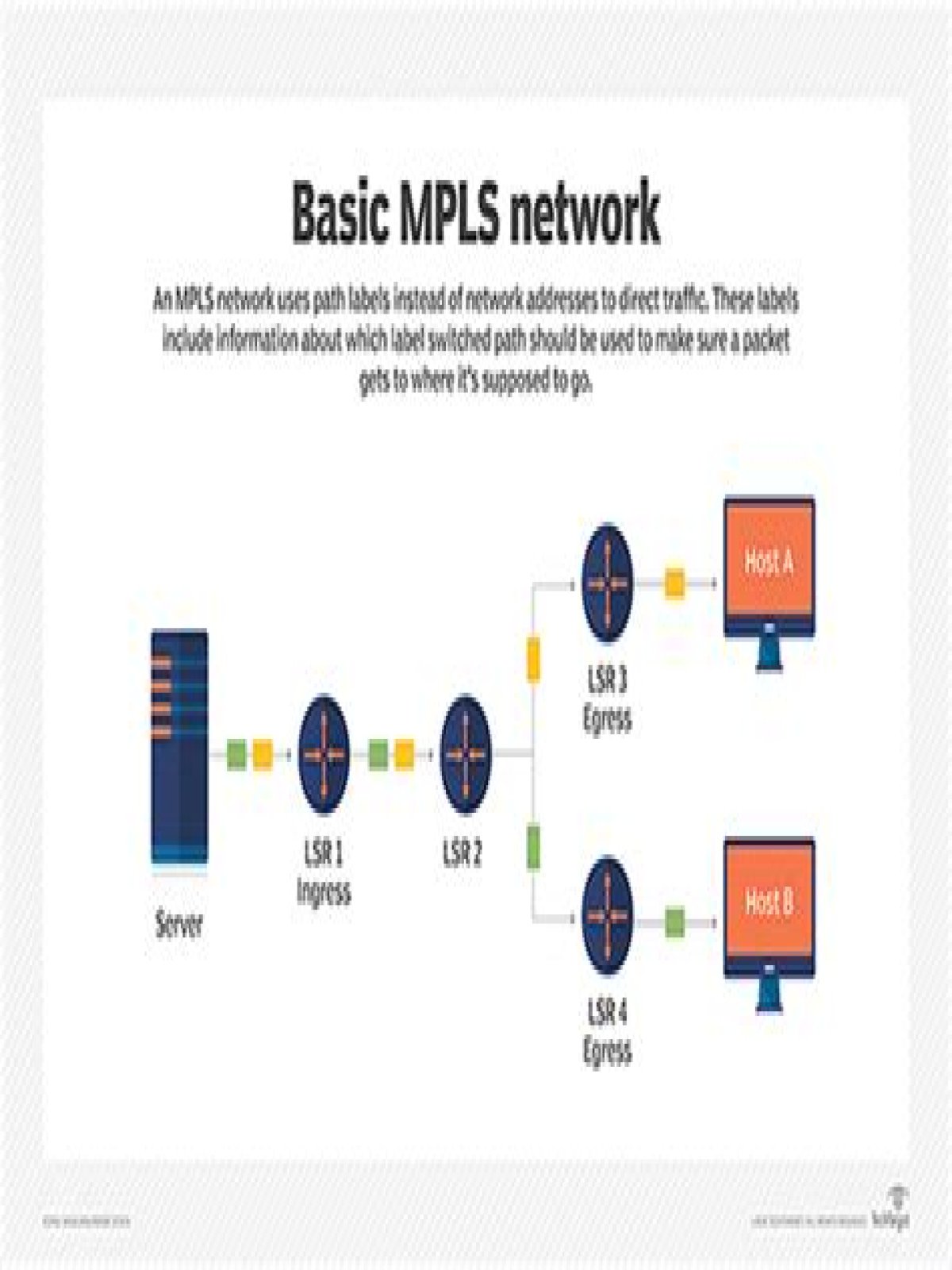
Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) converts routed network to something closer to a switched network and offers information transfer speeds that are not available in a traditional IP-routed network. Instead of forwarding packets on a hop-by-hop basis, paths are established for particular source-destination pairs.
Why is MPLS used?
In practice, MPLS is mainly used to forward IP protocol data units (PDUs) and Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS) Ethernet traffic. Major applications of MPLS are telecommunications traffic engineering, and MPLS VPN.
What MPLS basics?
MPLS directs data from one network node to the next based on short path labels rather than long network addresses, avoiding complex look-ups in a routing table. MPLS is also called Layer 2.5 as it resides between Layer 2 and Layer 3 of the OSI layer model.
What are the characteristics of MPLS?
21 MPLS Features You Need to Know [White Paper]
- #1 Internal BGP Internet Routing.
- #2 Burstable Bandwidth.
- #3 Real-Time Bandwidth Adjustment.
- #4 Hosted VoIP.
- #5 Voice.
- #6 Network Firewall.
- #7 Hosted Email & Content Filtering.
- #8 Hosted/Cloud Services.
What is the difference between BGP and MPLS?
BGP carries routing information for the network and MPLS labels, whereas MPLS transports the data traffic.
What is MPLS vs SD-WAN?
To summarize, while MPLS is a dedicated circuit, SD-WAN is virtual overlay and decoupled from physical links. This gives MPLS a slight advantage when preventing packet loss, but you’ll incur more expenses for every megabit transferred.
Why was MPLS created?
MPLS was created in the late 1990s as a more efficient alternative to traditional Internet Protocol (IP) routing, which requires each router to independently determine a packet’s next hop by inspecting the packet’s destination IP address before consulting its own routing table.
What are the prerequisites to run MPLS?
MPLS is a forwarding method, in which packets are forwarded based upon labels. It is called as Multi protocol because it is going to support all the protocols like Ethernet, ATM, Frame Relay and PPP.
What routing protocol is MPLS?
MPLS uses layer 3 service i.e, Internet Protocol, and uses router as forwarding device. The traffic of different customers is separated from each other because MPLS works somewhat like VPN.
What is the difference between SDH and MPLS?
MPLS-TP is virtually the packet-based alternative to “good old” SDH/SONET technology. This packet-based technology offers the same qualities of network stability and settings as SDH/SONET. By significantly reducing complexity, MPLS-TP makes life easier for network administrators.
Does MPLS require BGP?
These routers must be able to switch MPLS LSPs—that is, they function as MPLS label-switching routers (LSRs) and might function as label edge routers (LERs). Running BGP-4 on the P routers is not necessary to be able to exchange routing information for VPNs. Using MPLS is not necessary.
Why we use BGP instead of OSPF?
Scale: BGP is more flexible and scalable than OSPF and it is also used on a larger network. Preferred path: OSPF is used to determine the fastest route while BGP puts emphasis on determining the best path. Protocol: In OSPF, internet protocol is used. While in BGP, transmission control protocol is used.
What is MPLS and why do we need it?
Multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) is a technique for speeding up network connections that was first developed in the 1990s. The public Internet functions by forwarding packets from one router to the next until the packets reach their destination. MLPS, on the other hand, sends packets along predetermined network paths.
What does “MPLS” stand for?
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a routing technique in telecommunications networks that directs data from one node to the next based on short path labels rather than long network addresses, thus avoiding complex lookups in a routing table and speeding traffic flows.
What is MPLS in simple terms?
Multi Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) in simple terms, which enables a Service Provider (SP) to offer scalable and internetworking solutions for its clients. In addition to scalability, MPLS offers Traffic Engineering (TE) and Quality of Service (QoS).
What are the different types of MPLS?
Here is the best answer and explanation to 3 types of MPLS. MPLS is available in three types: Layer 2 point-to-point is a cost-effective way and a flexible alternative to high bandwidth leased lines. Many wholesale network operators have based their core network infrastructure on ethernet and use Layer 2.