Hiring an independent contractor: what forms do I need?
- Form W-9. Form W-9, the Request for Taxpayer Identification Number and Certification, is required to be completed by all contractors.
- A Written Contract.
- Invoices.
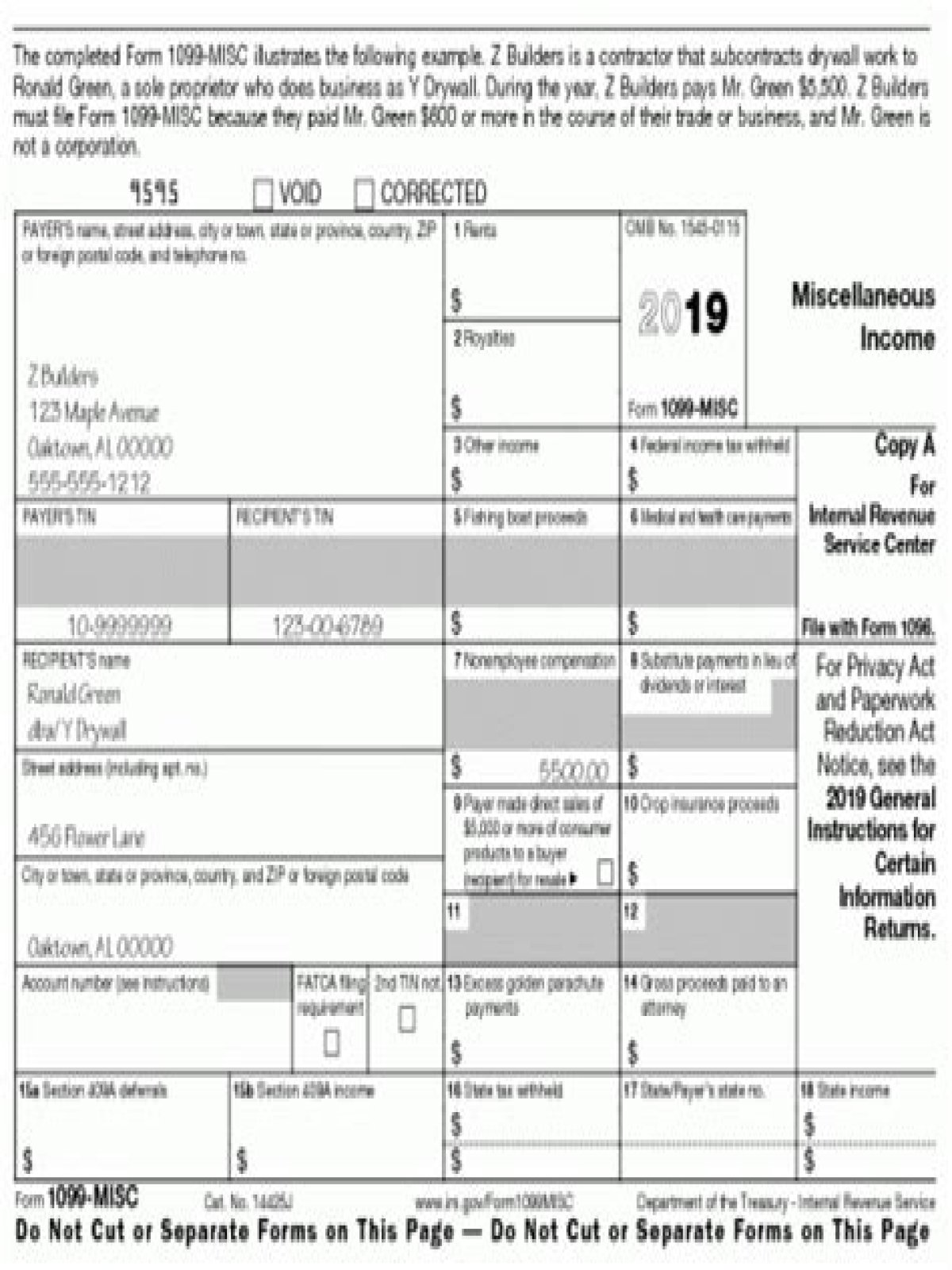
- Form 1099-MISC.
- Form SS-8?
What documents should I ask for when hiring a contractor?
Your general contractor should provide proof of licensing, bonding and insurance before a project starts, but it’s better to have it in hand before you sign any contracts. It’s important that contractors carry any licensing and/or certification required for the specific trade or skill they practice.
Do I need an EIN to hire an independent contractor?
Do I need an EIN to hire an independent contractor? Yes, you will need to get the EIN (Employer Identification Number) for your contractor’s business. If they provide individual services, a social security number will suffice.
What do you need to hire an independent contractor?
1 Form W-9. The IRS requires contractors to fill out a Form W-9, request for Taxpayer Identification Number and Certification, which you should keep on file for at least four years 2 Form 1099-MISC. 3 A Written Contract. 4 Invoices. 5 Independent Contractor vs. 6 Helpful Link
What kind of tax forms do you need for independent contractors?
You must have a W-9 on file for each independent contractor so that you don’t have to withhold income taxes from that individual. Then, you have the information to create a 1099-MISC form for that person for the tax year (similar to a W-2 form for employees).
What do you need to know before hiring a contractor?
Before you hire your contractor, you want to create an independent contractor agreement, which is a legal contract that explains your business relationship. Why? Because it’s important for all parties to get on the same page so time and resources aren’t wasted—and to minimize legal issues should your relationship get messy.
Why do companies classify employees as independent contractors?
Some companies will classify an employee as an independent contractor on purpose to reduce payroll and the cost of employee benefits such as vacation or overtime pay, bypass minimum wage laws, avoid employee income tax withholding, etc. However, these are rights that must belong exclusively to the employee.