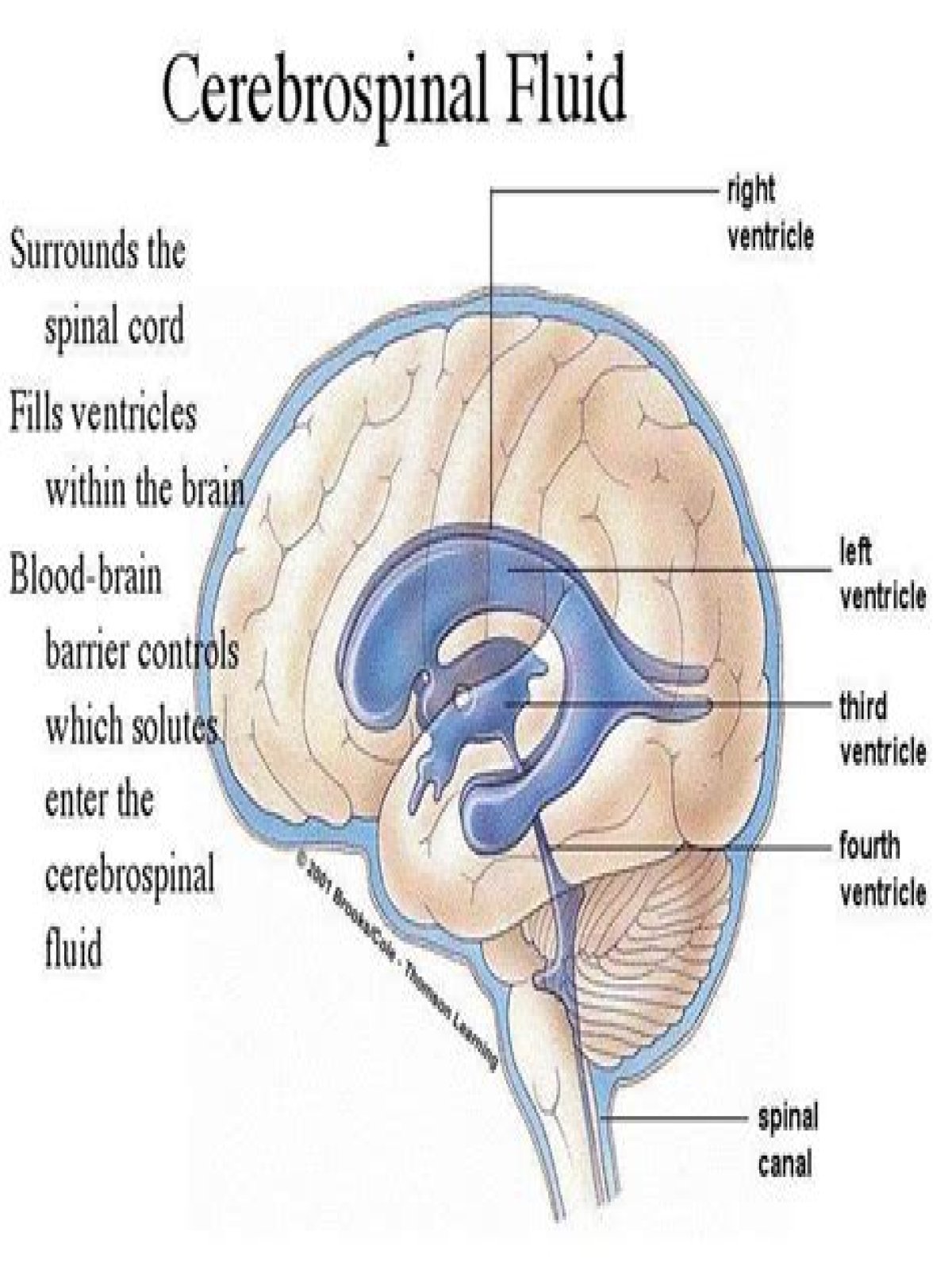
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colourless ultrafiltrate of plasma with low protein content and few cells. The CSF is mainly produced by the choroid plexus, but also by the ependymal lining cells of the brain’s ventricular system.
What cell type makes cerebrospinal fluid?
CSF is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexus of the ventricles of the brain, and absorbed in the arachnoid granulations.
What is the composition and function of cerebrospinal fluid?
CSF composition. CSF is a product of plasma filtration and membrane secretion, and so its composition is different from that of plasma. CSF, in general, is clear, colourless, nearly acellular, and has a low protein concentration. Various ions, enzymes, and other substances are also found in normal CSF.
What is the normal composition of CSF?
Normal Results CSF total protein: 15 to 60 mg/100 mL. Gamma globulin: 3% to 12% of the total protein. CSF glucose: 50 to 80 mg/100 mL (or greater than two thirds of blood sugar level) CSF cell count: 0 to 5 white blood cells (all mononuclear), and no red blood cells.
Where is cerebrospinal fluid made?
cerebral ventricles CSF formation. Most CSF is formed in the cerebral ventricles. Possible sites of origin include the choroid plexus, the ependyma, and the parenchyma[2]. Anatomically, choroid plexus tissue is floating in the cerebrospinal fluid of the lateral, third, and fourth ventricles.
Which type of cell helps regulate composition of CSF?
The secretion and composition of the CSF is tightly regulated by the CPs, which are complex structures comprised of a plexus of fenestrated capillaries surrounded by a layer of cuboidal epithelial cells, with an intervening stromal space between these two components (Fig. 1D).
Which cell type is most associated with the production and flow of cerebrospinal fluid?
The layer of ependymal-derived cells surrounding the blood vessels of the choroid plexus functions mainly to produce CSF. This is accomplished through the selective uptake of water and certain other molecules from the blood into the cells.
Which space contains CSF?
subarachnoid space The subarachnoid space consists of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), major blood vessels, and cisterns.
Does cerebrospinal fluid contain red blood cells?
Normally, there are no RBCs in the cerebrospinal fluid, and there should be no more than five WBCs per cubic millimeter of CSF. If your fluid contains RBCs, this may indicate bleeding. It is also possible that you had a traumatic tap (blood leaked into the fluid sample during collection).
Which type of Neuroglial cells help regulate the composition of cerebrospinal fluid?
Microglia are the smallest form of neuroglia and proliferate in response to injury. They increase in size as they phagocytose degraded matter. There are three different types of the last type of neuroglia, the ependyma. They line cavities of brain and spinal cord and maintain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow.
What is CSF chemistry?
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis is a group of laboratory tests that measure chemicals in the cerebrospinal fluid. CSF is a clear fluid that surrounds and protects the brain and spinal cord. The tests may look for proteins, sugar (glucose), and other substances.
What produces cerebrospinal fluid or CSF?
CSF is produced mainly by a structure called the choroid plexus in the lateral, third and fourth ventricles. CSF flows from the lateral ventricle to the third ventricle through the interventricular foramen (also called the foramen of Monro).
What is cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is an ultrafiltrate of plasma contained within the ventricles of the brain and the subarachnoid spaces of the cranium and spine. It performs vital functions, including providing nourishment, waste removal, and protection to the brain. [2]
What is the composition of CSF?
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colourless ultrafiltrate of plasma with low protein content and few cells. The CSF is mainly produced by the choroid plexus, but also by the ependymal lining cells of the brain’s ventricular system. Click to read further detail. Regarding this, what is the normal composition of CSF?
What is the vascular source of cerebrospinal fluid?
The cerebrospinal fluid is produced by vascular bulges, called choroid plexuses. The choroid plexuses are located in the lateral ventricles (along the line of the choroid fissure) and in the roof of the third and fourth ventricles. The vascular source of the choroid plexus differs between the lateral and third ventricles, and the fourth ventricle.
Why does the cerebrospinal fluid sink?
The “sink” action of the CSF arises from the restricted access of water-soluble substances to the CSF and the low concentration of these solutes in the CSF. Therefore, solutes entering the brain, as well as those synthesized by the brain, diffuse freely from the brain interstitial fluid into the CSF.