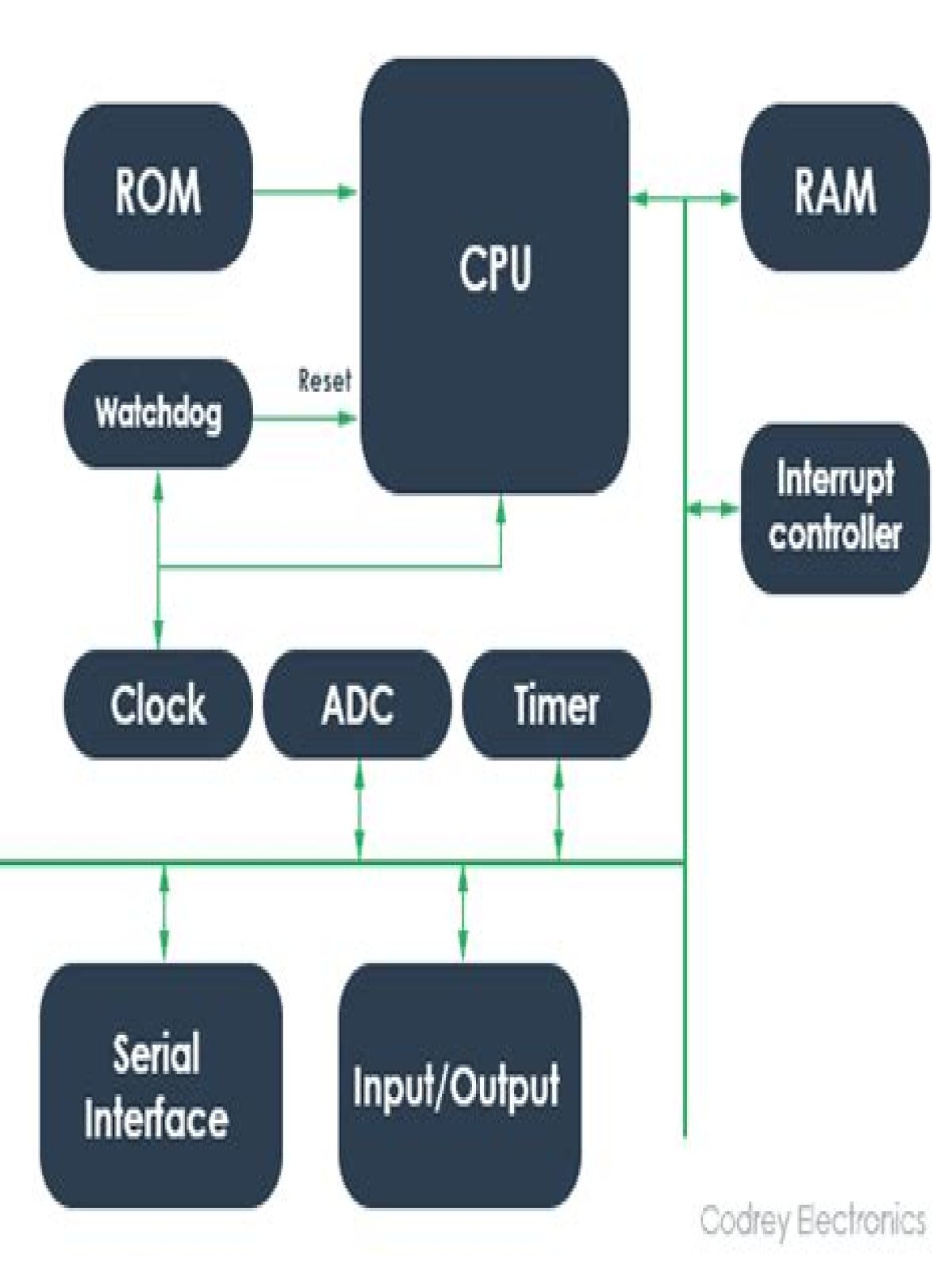
Core microcontroller components include:
- CPU (Central Processing Unit).
- RAM (Random Access Memory).
- ROM (Read-Only Memory).
- Internal Oscillator (the main timer of the MCU).
- I/O (Input/Output) Ports.
- Peripheral Controller Chips (other optional accessories and components).
- What is microprocessor and Microcontroller?
- What are different types of micro controllers?
- What is micro controller unit?
- What is difference between microprocessor and microcomputer?
- What is the difference between microcomputer and microcontroller?
- What is timer in microcontroller?
- What is MCU and its types?
- What is a microcontroller and why do I need one?
- What are the building blocks of a microcontroller?
- How does a microprocessor work?
What is microprocessor and Microcontroller?
Brief overview: Microprocessor consists of only a Central Processing Unit, whereas Micro Controller contains a CPU, Memory, I/O all integrated into one chip. The microprocessor uses an external bus to interface to RAM, ROM, and other peripherals, on the other hand, Microcontroller uses an internal controlling bus.
What are 3 basic applications of a Microcontroller?
Microcontroller Applications:
- Light sensing & controlling devices.
- Temperature sensing and controlling devices.
- Fire detection & safety devices.
- Industrial instrumentation devices.
- Process control devices.
What are different types of micro controllers?
Different types of Microcontroller Programming used in Embedded Systems
- Advantages. A microcontroller is a cheap and minimal size, easy to carry out.
- PIC Microcontroller.
- ARM Microcontroller.
- 8051 Microcontroller.
- AVR Microcontroller.
- MSP Microcontroller.
What is micro controller unit?
A microcontroller (MCU for microcontroller unit) is a small computer on a single metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) integrated circuit (IC) chip. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals.
What is the function of a micro controller?
Microcontroller is a compressed micro computer manufactured to control the functions of embedded systems in office machines, robots, home appliances, motor vehicles, and a number of other gadgets. A microcontroller is comprises components like – memory, peripherals and most importantly a processor.
What is difference between microprocessor and microcomputer?
A microprocessor is a computer processor wherein the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. A microcomputer is a small, relatively inexpensive computer with a microprocessor as its central processing unit (CPU).
What is the difference between microcomputer and microcontroller?
A microcomputer consists of microprocessor, memory, input device and output device. A microcontroller is a programmable device that includes microprocessor, memory and I/O signal lines on a single chip, fabricated using VLSI technology. Microcontrollers are also known as single microcomputers.
What is the application of micro controller?
In the office, microcontrollers are used in computer keyboards, monitors, printers, copiers, fax machines, and telephone systems to name a few. In your home, microcontrollers are used in microwave ovens, washers and dryers, security systems, lawn sprinkler station controllers, and music/video entertainment components.
What is timer in microcontroller?
A timer is a specialized type of clock which is used to measure time intervals. A counter is a device that stores (and sometimes displays) the number of times a particular event or process occurred, with respect to a clock signal. It is used to count the events happening outside the microcontroller.
What is MCU and its types?
Microcontrollers Types & Their Applications. A microcontroller is a single chip and it is denoted with μC or uC. The fabrication technology used for its controller is VLSI. The different components used in a microcontroller are a processor, peripherals, & memory.
Why microcontroller is used?
Microcontrollers are used in automatically controlled products and devices, such as automobile engine control systems, implantable medical devices, remote controls, office machines, appliances, power tools, toys and other embedded systems.
What is a microcontroller and why do I need one?
Wearables and dozens of real time applications use a microcontroller other than a microprocessor for their core design of the entire product. And, these days almost every electronic device comes with a microcontroller.
What are the building blocks of a microcontroller?
The memory size varies for different microcontroller families. They are often referred as “ On-Chip microcomputer ” in some cases. The building blocks of the microcontroller are the processor, memory, and peripherals. Let’s discuss a bit more in detail. Here is the inside view of microcontroller architecture.
Do microcontrollers require any external interfacing?
No need for any external interfacing of basic components like Memory, I/O Ports, etc. Microcontrollers doesn’t require complex operating systems as all the instructions must be written and stored in the memory. (RTOS is an exception). All the Input/Output Ports are programmable.
How does a microprocessor work?
The microprocessor can be programmed to perform functions on specified/given data by writing specific instructions into its memory. The microprocessor reads one instruction at a time, matches it with its instruction set, and performs the data manipulation specified. The result is either stored back into memory or displayed on an output device.