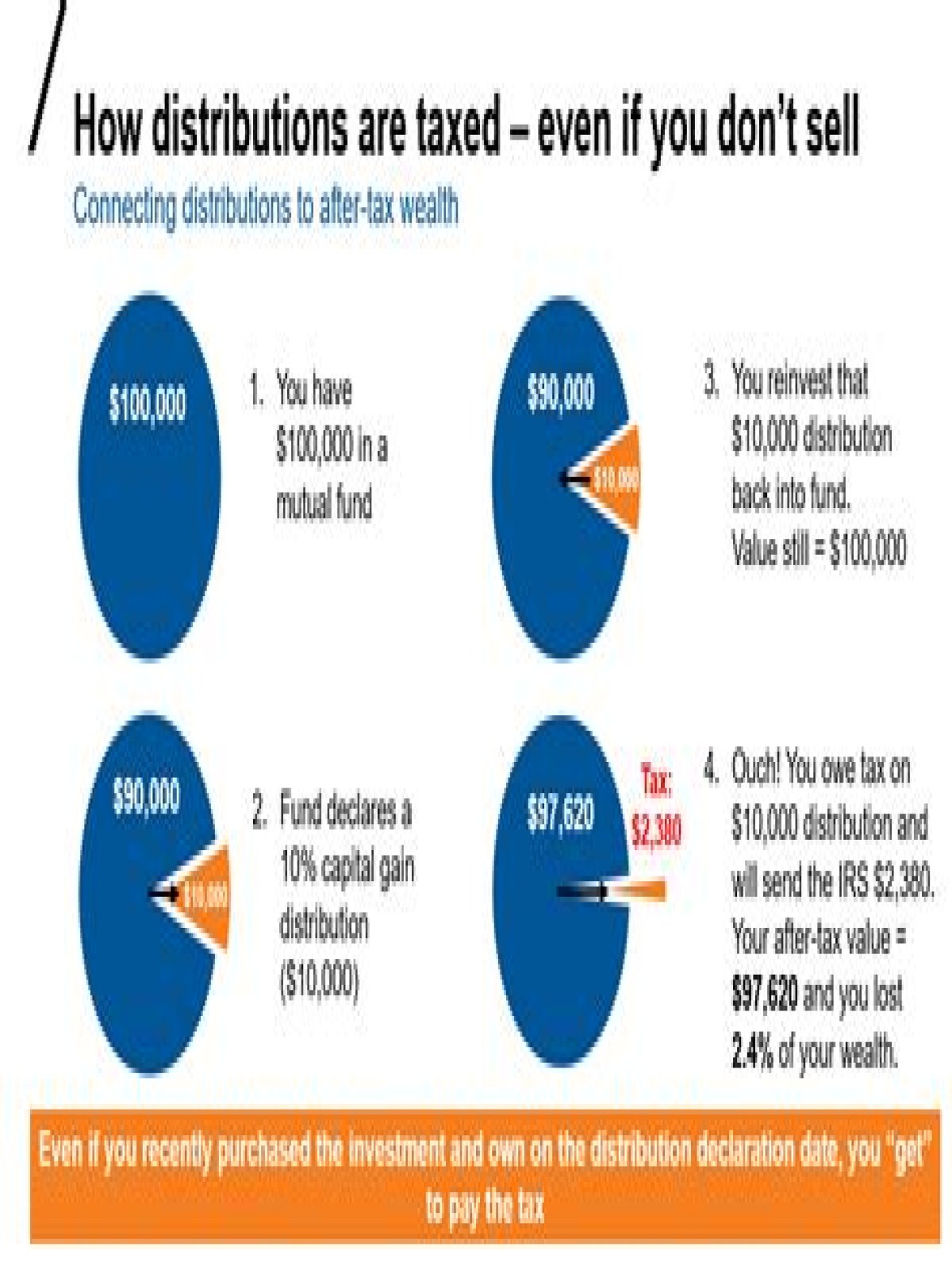
Under current IRS regulations, capital gains distributions are taxed as long-term capital gains, no matter how long the individual has owned shares of the fund. That means a tax rate of 0%, 15%, or 20%, depending on the individual’s ordinary income tax rate.
What is a capital gain distribution and how is it taxed?
Long-term capital gain distributions are taxed at long-term capital gains tax rates; distributions from short-term capital gains and net investment income (interest and dividends) are taxed as dividends at ordinary income tax rates. Ordinary income tax rates generally are higher than long-term capital gains tax rates.
Are capital gains taxed higher than ordinary income?
A realized capital gain is the money from the sale of a capital asset (stock, real estate) at a price higher than the one you paid for it. The most important thing to understand is that long-term realized capital gains are subject to a substantially lower tax rate than ordinary income.
Do capital gains distributions count as income?
These capital gain distributions are usually paid to you or credited to your mutual fund account, and are considered income to you. Form 1099-DIV, Dividends and Distributions distinguishes capital gain distributions from other types of income, such as ordinary dividends.
How are short term capital gain distributions taxed?
Short-term capital gains distributions are taxed at the shareholder’s ordinary income tax rate. Depending upon income level and filing status, this rate can range from 10% up to 39.6%. Long-term gains get taxed at the long-term capital gains rate. Taxpayers in the two lowest brackets, 10% and 15%, pay no long-term gains tax.
How are long term capital gains and dividends taxed?
Where do capital gains go on a tax return?
Short-term capital gains distributions are lumped together with any dividend and income distributions and appear under the total ordinary dividends column. Long-term capital gains distributions appear under the total capital gains distributions column and may need to be reported on the IRS’s Schedule D form when filing taxes.
How is a capital distribution from a company taxed?
A capital distribution from a company is any money that’s paid from the company to its shareholders that is subject to capital gains tax and is not treated as income for income tax purposes. The majority of distributions made by a company are in the form of income distributions, such as dividend payments, and will be subject to income tax.