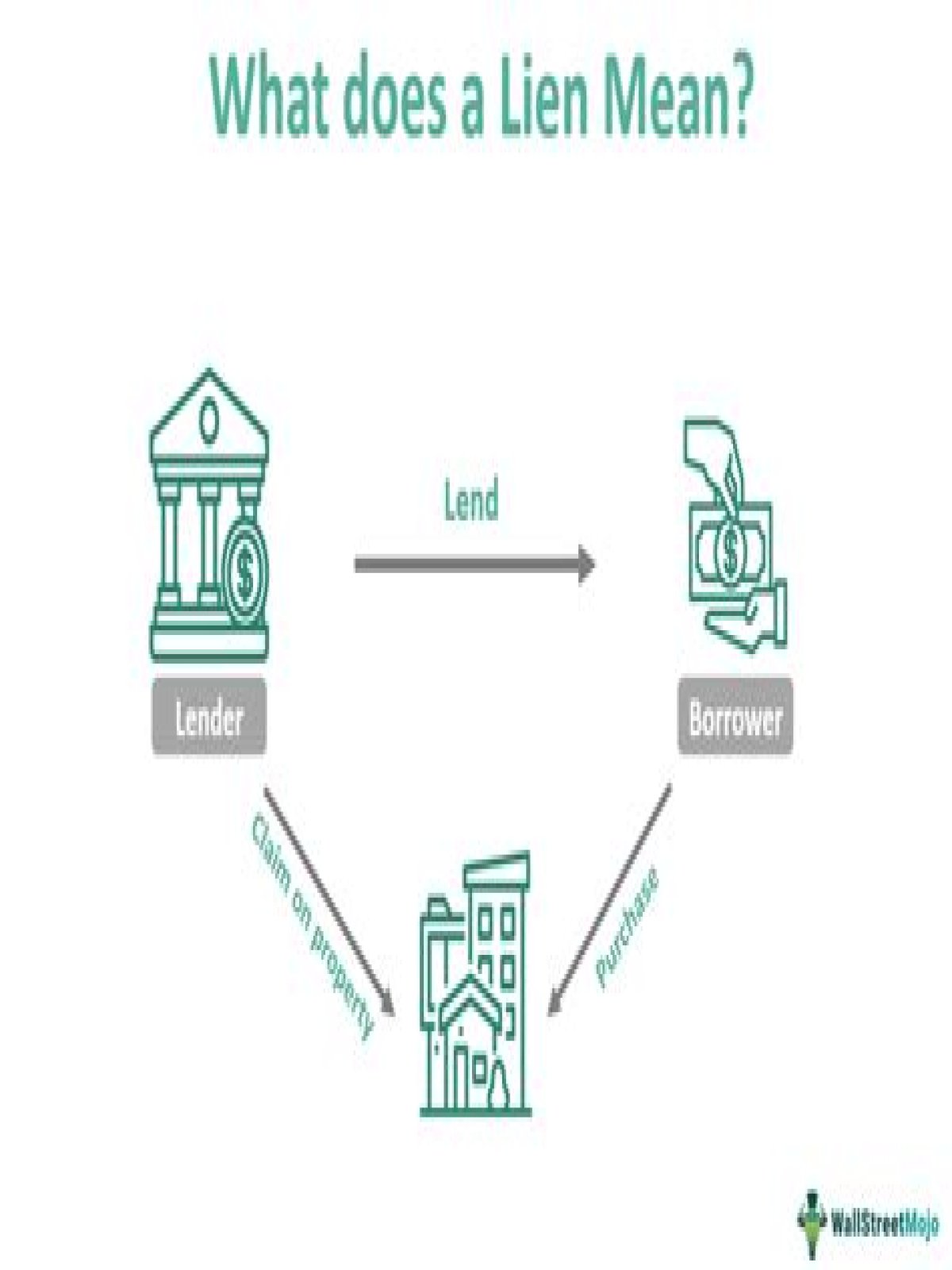
A lien is a legal tool creditors use to stake a claim to an asset you’re using as debt collateral. Liens are used as a backup to help safeguard lenders’ investments, but can also be used as a remedy for creditors to collect unsatisfied debts.
What does record lien mean?
A “lien” is a notice that attaches to your property, telling the world that a creditor claims you owe it some money. A lien is typically a public record.
Where does a lien go on a credit report?
Since 2018, tax, judgment and mechanic liens haven’t been included on the credit reports maintained at the three consumer credit bureaus (Experian, TransUnion and Equifax). In the case of real estate liens, the lien itself isn’t recorded in your reports, but the mortgage for which the lien is held is listed as one of your credit accounts.
How long does a tax lien stay on your credit report?
The normal credit reporting time limit doesn’t apply for unpaid tax liens. They can remain on your credit report indefinitely, but a credit bureau might remove it within 10 to 15 years, depending on their policies. Unfortunately, this is discretionary, not mandatory.
How are mechanic’s liens noted on your credit record?
Different states have different legal requirements and statuses for mechanic’s liens, and in some states mechanic’s liens are not noted as “judgments” and are only noted in the public record in relation to the property and not the property owner, and thus do not automatically appear on the property owner’s credit record.
How does a lien on your property affect your credit?
A creditor may place a lien against your personal property, such as your house or car. The creditor files for a property lien in court, so the public record appears on your credit report. A public record like a lien has a negative effect on your credit score and may also affect whether or not a lender extends credit to you.