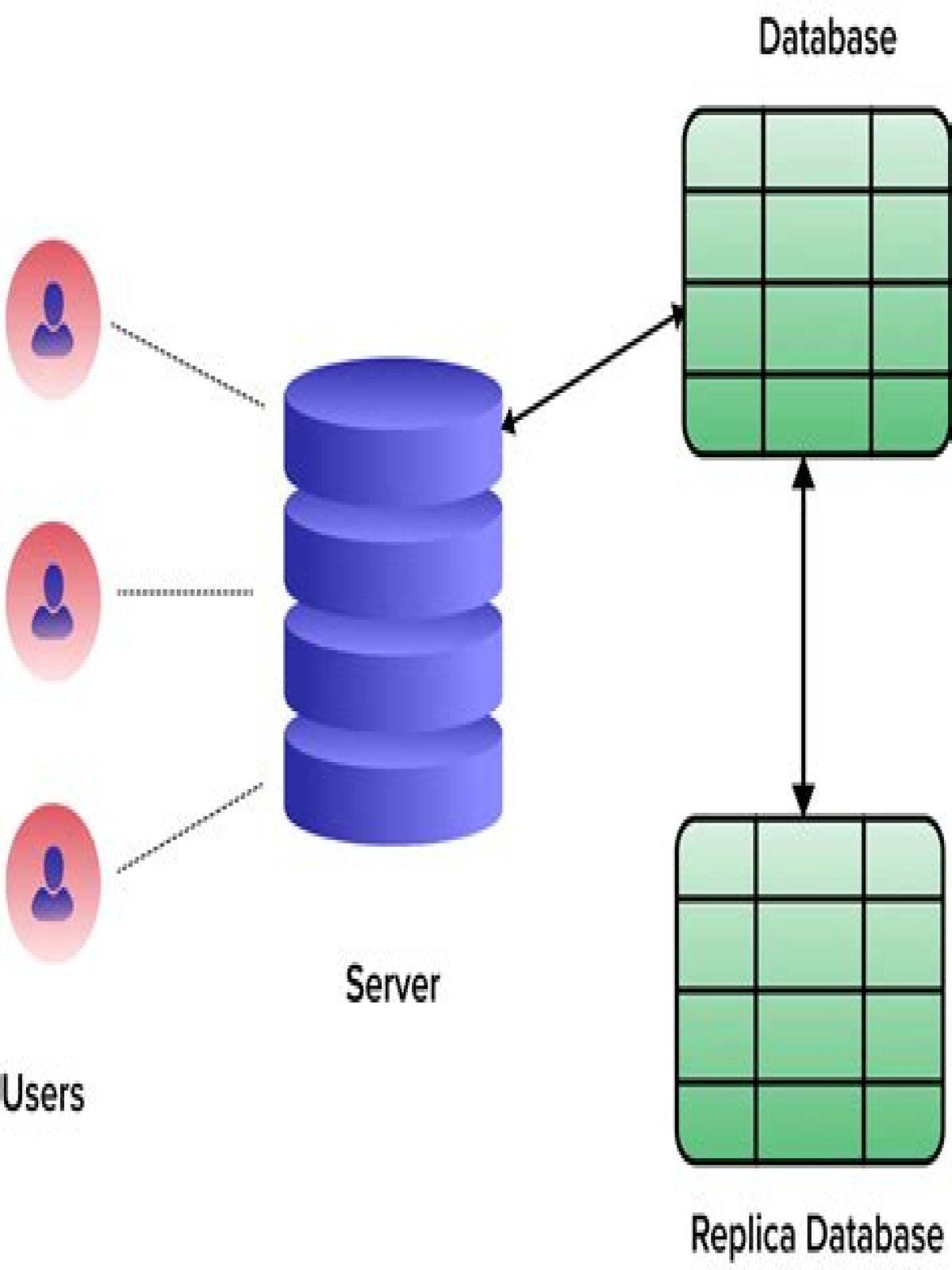
Data replication is the process of making a copy of data and storing it in a separate location to enable disaster recovery or to improve accessibility.
What is replication in NetWorker?
Data replication is the process of copying data from one location to another. Replication can take place over a storage area network, local area network or local wide area network, as well as to the cloud.
What is Mtree replication?
Mtree replication allows an mtree to be copied in its entirety between two Data Domain systems. Mtree replication can be used to provide a DR position, additional resiliency for a source Data Domain or to migrate from one unit to another.
How do you stop replication in data domain?
This will not require a reboot, however, existing TCP connections are not affected, so we will need to restart our replication. Exit SE mode. At this point, you can monitor the replication, and most likely, the issue will be taken care of – assuming no physical network issues.
How does data replication work?
How data replication works. Replication involves writing or copying the same data to different locations. For example, data can be copied between two on-premises hosts, between hosts in different locations, to multiple storage devices on the same host, or to or from a cloud-based host.
How does data Domain deduplication work?
How data deduplication works
- How data deduplication works.
- Deduplication segments an incoming data stream, uniquely identifies data segments, and then compares the segments to previously stored data. If the segment is unique, it’s stored on disk.
What is an MTree Data Domain?
DataDomain MTree Dell EMC defines an MTree as logical partitions of the file system and they are identified by a unique name. MTrees are used to create (protocols can be mixed, except VTL): DD Boost storage units.
How does deduplication work in Data Domain?
Deduplication segments an incoming data stream, uniquely identifies data segments, and then compares the segments to previously stored data. If the segment is unique, it’s stored on disk.
What is clone controlled replication?
Cloned Controlled Replication (CCR) is another feature of DDBoost that is useful when integrating NetWorker and Data Domain through DDBoost. With CCR, replication of NetWorker save sets between two Data Domain systems can be started, monitored, and tracked through cloning operations in NetWorker.
What types of replication are available in domain native?
Data Domain Native replication has three replication types, which are Directory, Mtree and Collection. They are copying the entire directory, or the file system. Once configured and initialized, the replication will automatically run.
What is mtree replication and how does it work?
Mtree replication allows an mtree to be copied in its entirety between two Data Domain systems. The mtree replication will only copy blocks from the source to the target which do not exist on the target. Mtree replication can be used to provide a DR position, additional resiliency for a source Data Domain or to migrate from one unit to another.
How to use DD replication?
If you want to use DD replication, you need to install replication license at the source DD system and target DD system. 1) It only copies the deduplication and compression data. 2) In the replication, source device will send Index of replication data to the target device.
What is the difference between mtree replication and Veeam copy?
Re: DATA DOMAIN Mtree replica. With Mtree replication the offsite replica is a read-only mirror of the source. With Veeam Copy you should ideally have a Veeam proxy acting as a gateway server to Data Domain at each site and utilise DDBoost.