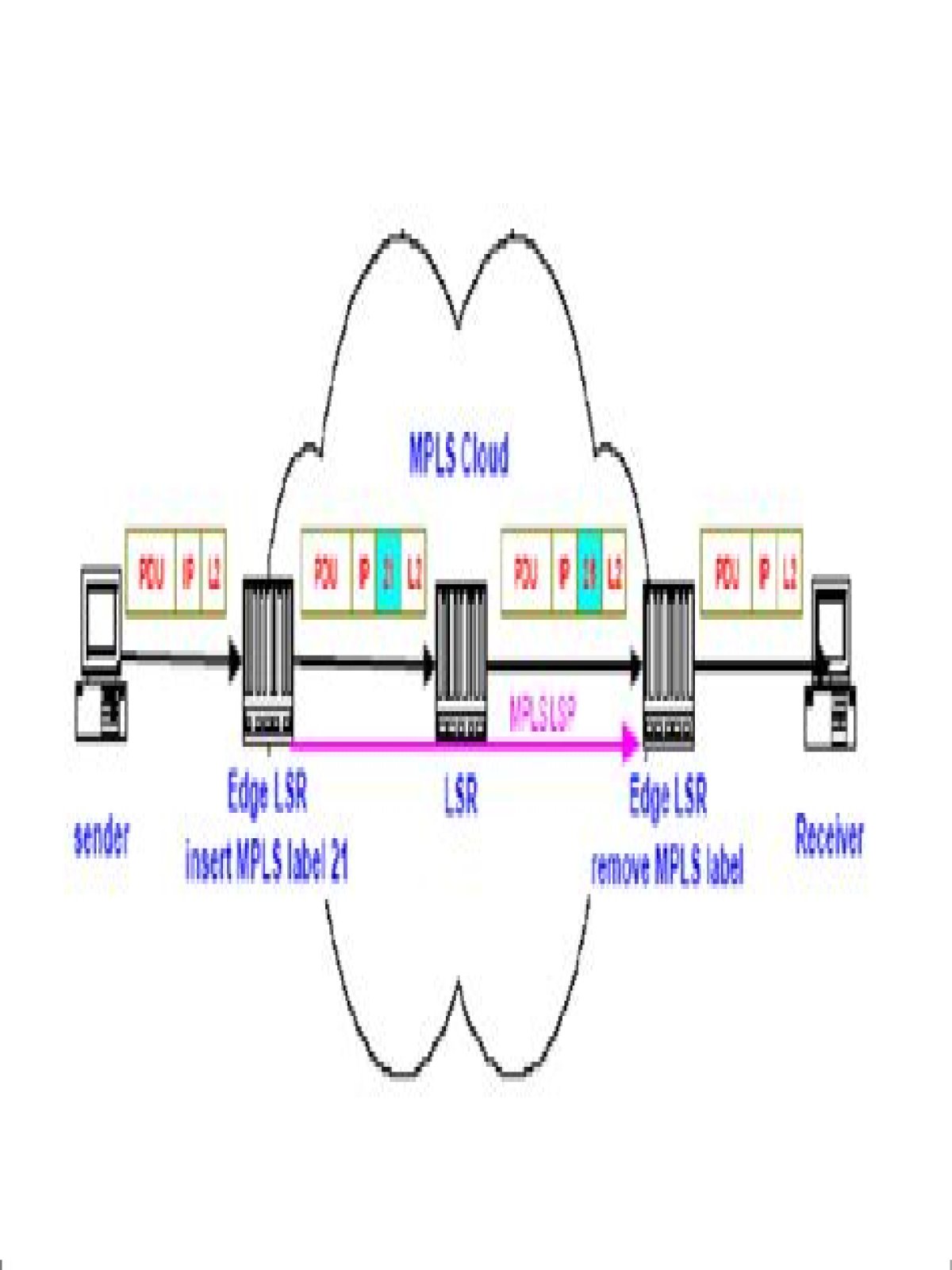
An MPLS FEC consists of a set of packets that are all forwarded in the same manner by a given label-switching router (LSR). For example, all packets received on a particular interface might be assigned to a FEC.
What is the role of label forwarding information base LFIB in MPLS?
MPLS creates its own database for lookups called the Label Forwarding Information Base (LFIB), but it uses the CEF FIB as a source of this information. If CEF cannot resolve a route, the label cannot switch to a destination either.
How does MPLS label switching work?
What is the “label switching” in MPLS routing? As packets travel through the MPLS network, their labels are switched or swapped. The packet enters the edge of the MPLS backbone, is examined, classified and given an appropriate label, and forwarded to the next hop in the pre-set Label Switched Path (LSP).
How are forwarding decisions made with MPLS?
In an MPLS network, labels are assigned to data packets. Packet-forwarding decisions are made solely on the contents of this label, without the need to examine the packet itself. This allows one to create end-to-end circuits across any type of transport medium, using any protocol.
What is an MPLS forwarding equivalence class?
A forwarding equivalence class (FEC) is a term used in Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) to describe a set of packets with similar or identical characteristics which may be forwarded the same way; that is, they may be bound to the same MPLS label.
What are the two types of MPLS labels?
MPLS Label Distribution – LDP Part2
- MPLS Reserved Labels Range. Labels 0 through 15 are reserved labels.
- Implicit NULL Label (Label3) The implicit NULL label is the label that has a value of 3.
- Explicit NULL Label (Label 0 V4/ 2 V6)
- Router Alert Label (Label 1)
What is the difference between FIB and LFIB?
The LFIB is essentially the label routing table. Labels are shared through distribution protocols, but the information is built based on the IP routing table information. This information is stored in the Forwarding Information Base (FIB) and Label Forwarding Information Base (LFIB).
How is label forwarding different from IP switching?
Label switching is a technique of network relaying to overcome the problems perceived by traditional IP-table switching (also known as traditional layer 3 hop-by-hop routing). The switching is much faster than IP-routing. New technologies such as Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) use label switching.
Will SD-WAN replace MPLS?
Yes! SD-WAN provides similar performance and reliability to a dedicated MPLS circuit. However, it accomplishes this by aggregating various transport media and optimizing traffic routing rather than relying upon predefined, dedicated links.
How labels are assigned in MPLS?
An incoming labeled packet is forwarded using the LFIB table where the incoming (locally significant) label 5 is swapped with the next-hop label 3. A new protocol is introduced into MPLS-enabled networks to exchange labels assigned to IP destination networks.
What information is contained in the LFIB?
The LFIB is essentially the label routing table. Labels are shared through distribution protocols, but the information is built based on the IP routing table information. If the IP network experiences convergence issues or other types of instability, the MPLS network will be affected in a like manner.