Open-drain outputs can be useful for analog weighting, summing, and limiting as well as digital logic. An open drain terminal is connected to ground when a high voltage (logic 1) is applied to the gate, yet presents a high impedance when a low voltage (logic 0) is applied to the gate.
Why is it called open drain?
The term “open drain” means there’s a current sink, but on a FET device, for example, a MOSFET. The transistor will switch to ground when it’s active, thus “sinking” current (i.e., connecting to ground and thus current is shunted to ground for “recycling” in the ground plane).
What does it mean for a driver to be open drain?
Both SCL and SDA lines are “open drain” drivers. What this means is that the chip can drive its output low, but it cannot drive it high. For the line to be able to go high you must provide pull-up resistors to the 5v supply.
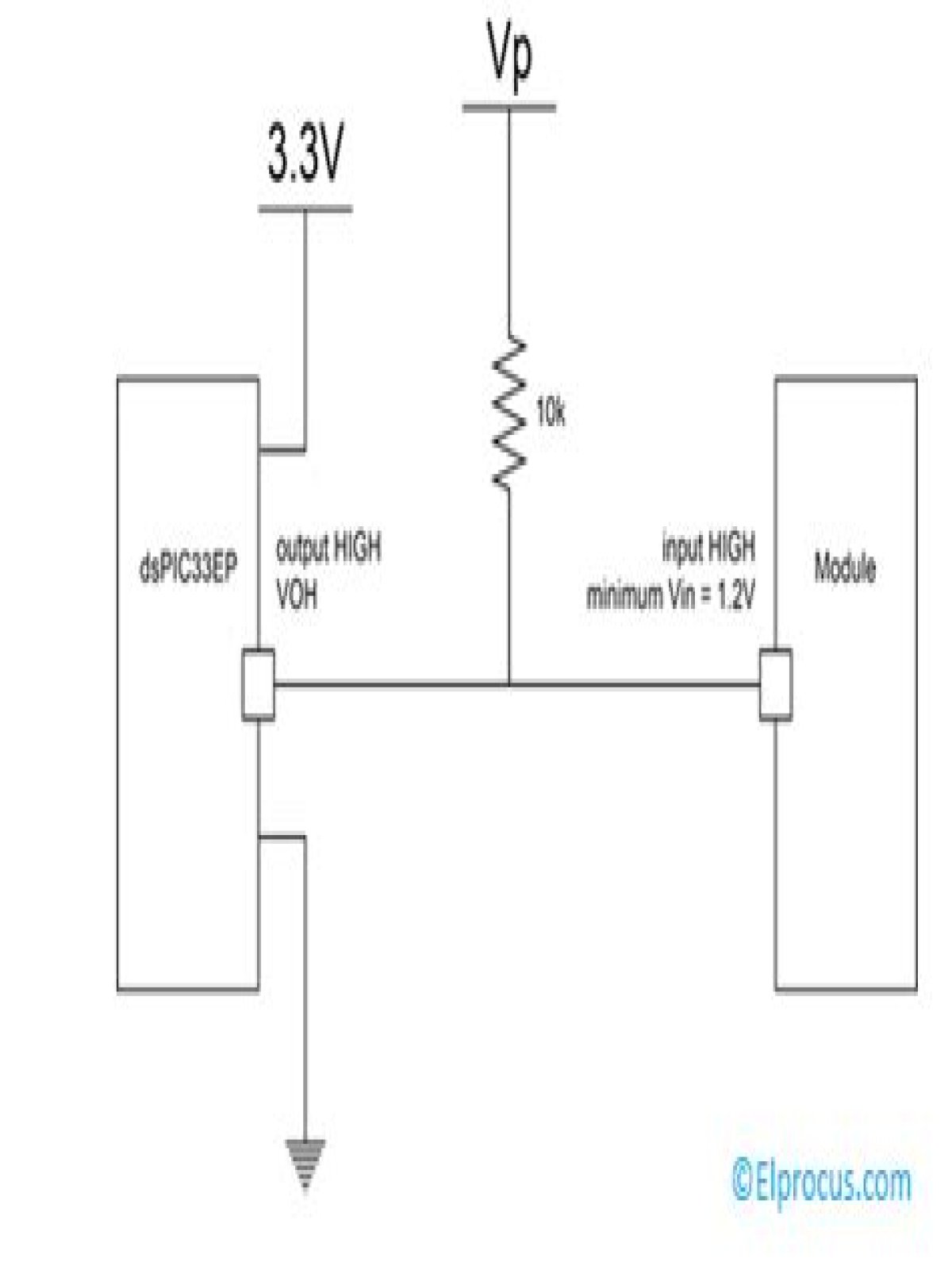
Is open drain high impedance?
Open-drain outputs are useful when multiple gates or pins are connected together, such as with the I2C bus. When a device is not using the bus, the open-drain output is in high-impedance mode and the voltage level is pulled high by the pull-up resistor.
What is open drain and open source?
What is an Open Drain : Configuration & Its Working. An open-drain or open-collector output pin is simply a transistor that is connected to the ground. Whenever we apply high input at the gate, drain, and source are shorted. Whenever we apply low input at the gate, drain, and source are disconnected.
Why is push pull faster than open drain?
Open drain output has higher power consumption during active transfers due to the pull-up resistors that are used. In general, the push-pull output has faster slopes than the open drain output.
What is open drain GPIO?
The DS2413 outputs are “Open Drain”. What that means is that the output is the “Drain” of an N-channel FET: Internally, the “Source” of the FET is connected to Ground. But the Drain is left open. When switched on, the FET provides a path for current to flow from the output pin to ground.
Is open collector sinking or sourcing?
While the NPN open collector transistor circuit produces a “current-sinking” output, that is the NPN transistors open collector terminal will sink the current to ground (0V), a PNP-type transistor can also be used in an open collector configuration to produce what is called a “current-sourcing” output.
What is the advantage of open drain output over push-pull output?
What is the advantage of open collector output?
The advantage of open-collector outputs, or open-drain outputs is that the load to be switched or controlled can be connected to a voltage supply which is independant, and/or different from the supply voltage used by the controlling circuit, and that they can “sink” or “source” an externally-supplied voltage depending …