Through a process of labelling the individual is forced to play the role of deviant. As a reaction to this role assignment (“You are criminal!”), the labelled person adapts his behaviour according to the role assigned to him (“Then I am criminal!”). This behaviour reaction is called secondary deviance.
- What is secondary deviance example?
- What is secondary deviance and how does it occur according to labeling theorist?
- What is primary and secondary deviance?
- What are the two types of deviance associated with labeling theory?
- What is secondary deviance quizlet?
- What causes secondary deviance?
- What is an example of secondary group?
- Why is secondary deviance in sociology important?
- Which is polygenic primary or secondary deviance?
- Which of the following is a characteristic of a pluralistic society?
- How does the labeling theory explain juvenile delinquency?
- What is the difference between primary deviation and secondary deviation according to lemert labeling theory?
- What are the different types of labeling theories?
- What is an example of labeling theory on deviance?
- Does labeling cause deviance?
- What is lemert's Labelling theory?
- What is primary deviation how does it differ from secondary deviation?
- What is secondary deviance group of answer choices?
- How does primary deviance different from secondary deviance quizlet?
- Under what circumstances does a deviant label transition from primary to secondary deviance?
- What do you understand by secondary group?
- What is labeling theory in sociology?
- What is the function of secondary group?
- What are secondary groups explain its characteristics?
- What is the importance of secondary group?
- What does tertiary deviance mean?
- What are the concepts of Labelling theory?
- What is the difference between positive and negative deviance?
- What is the pluralistic theory?
What is secondary deviance example?
Secondary deviance is a stage in a theory of deviant identity formation. … For example, if a gang engaged in primary deviant behavior such as acts of violence, dishonesty or drug addiction, subsequently moved to legally deviant or criminal behavior, such as murder, this would be the stage of secondary deviance.
What is secondary deviance and how does it occur according to labeling theorist?
Secondary deviance is when someone makes something out of that deviant behavior, which creates a negative social label that changes a person’s self-concept and social identity. … The consequences are not because of the act itself, but because of someone finding out about his behavior and labeling him.
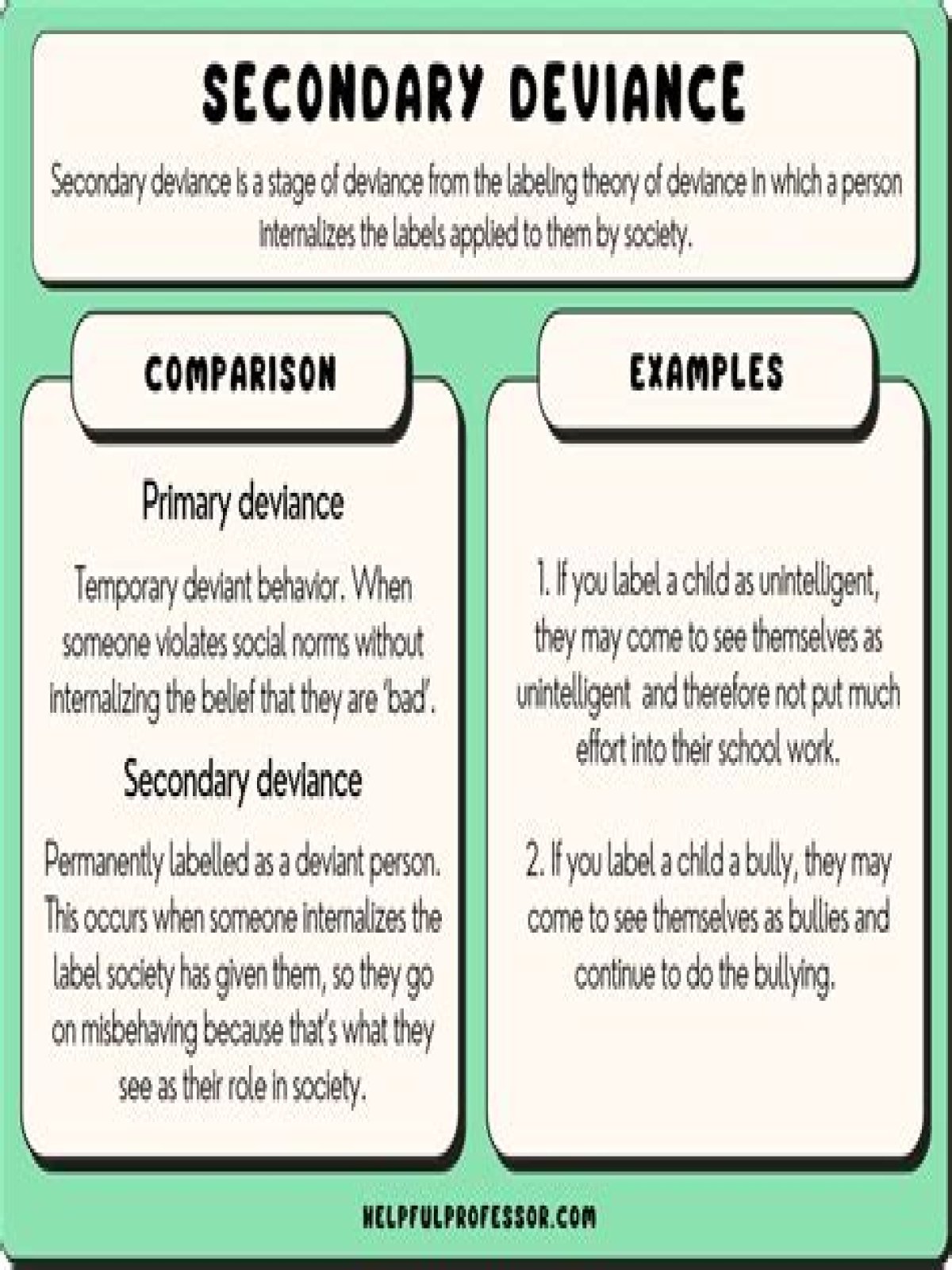
What is primary and secondary deviance?
Primary deviance refers to the initial act of deviance. If the person continues to veer away from acceptable behavior, then their actions are titled secondary deviance. This is when deviant behavior is long lasting and becomes part of one’s reputation.What are the two types of deviance associated with labeling theory?
Explain the two types of deviance associated with labeling theory. Primary deviance: this is nonconformity that goes undetected by those in authority. Secondary deviance: this results in the individual being labeled as deviant and accepting the label as true. The explanation of deviance as a learned behavior.
What is secondary deviance quizlet?
Secondary deviance occurs if the label from primary deviance sticks. The taking on a deviant identity by talking, acting, or dressing in a different way, rejecting the people who are critical, and repeatedly breaking the rules.
What causes secondary deviance?
Secondary deviance is triggered by reactions that follow the primary deviance. The social reaction to deviant behaviour ensures that the deviant is stigmatised. These social reactions include the deviant being labelled as criminal.
What is an example of secondary group?
Secondary groups are also groups in which one exchanges explicit commodities, such as labor for wages, services for payments, etc. Examples of these would be employment, vendor-to-client relationships, a doctor, a mechanic, an accountant, and such.Why is secondary deviance in sociology important?
Secondary deviance is much more significant because it alters a person’s self-regard and social roles. This follows the public identification of a person as deviant, and the individual’s response to this negative societal reaction (a judgement of social ‘normality’).
What is the difference between primary and secondary deviance which of the two is caused by labeling?The difference between primary deviance and secondary deviance is in how the deviant self-identifies after society labels his actions as deviations from the norm. Primary deviance is the first event that is punished. … This is secondary deviance.
Article first time published onWhich is polygenic primary or secondary deviance?
The Theory Primary deviance– “polygenic, arising out of a variety of social, cultural, psychological, and physiological factor.” Secondary deviance- secondary deviance is considered the deviant behavior itself.
Which of the following is a characteristic of a pluralistic society?
Anything pluralistic involves a diversity of different ideas or people. A pluralistic society is a diverse one, where the people in it believe all kinds of different things and tolerate each other’s beliefs even when they don’t match their own.
How does the labeling theory explain juvenile delinquency?
Labeling refers to the action of control agents or agencies that categorizes adolescent miscreants as delinquents. Such action is viewed by labeling theorists as a factor in increasing a juvenile’s sense of alienation from normative society, thus fueling deviant behaviors.
What is the difference between primary deviation and secondary deviation according to lemert labeling theory?
Primary deviance refers to the violation of a norm or rule that does not result in the violator’s being stigmatized as deviant, but secondary deviance refers to a deviant behaviour that is a result of being publicly labelled as deviant and treated as an outsider.
What are the different types of labeling theories?
There are three major theoretical directions to labeling theory. They are Bruce Link’s modified labeling, John Braithwaite’s reintegrative shaming, and Ross L. Matsueda and Karen Heimer’s differential social control.
What is an example of labeling theory on deviance?
For example, a person who volunteers to stay late at work is usually seen as worthy of praise, but, if a person has been labelled as a thief, people might be suspicious that they will steal something. For some people once a deviant label has been applied this can actually lead to more deviance.
Does labeling cause deviance?
Labeling could have either negative or positive consequences; but typically labeling theory is associated with negative consequences, and usually revolves around deviance. … This process of labeling can have an “effect on a person’s social identity” that they will carry with them for a lifetime” (Inderbitzen 331).
What is lemert's Labelling theory?
Lemert postulated that after someone carries out a deviant act (primary deviance) the reaction of others can lead to further (secondary) deviance. This idea was developed further by Aaron Cicourel (1968) in his famous study Power and the Negotiation of Justice.
What is primary deviation how does it differ from secondary deviation?
Primary deviation refers to differentiation which is relatively insignificant, marginal, and fleeting: individuals may drift in and out of it. Secondary deviation is deviance proper. It is a pivotal, central, and engulfing activity to which a person has become committed.
What is secondary deviance group of answer choices?
Secondary deviance occurs when a person’s self-concept and behavior begin to change after his or her actions are labeled as deviant by members of society. The person may begin to take on and fulfill the role of a “deviant” as an act of rebellion against the society that has labeled that individual as such.
How does primary deviance different from secondary deviance quizlet?
Primary deviance is the violation of a norm, but secondary deviance is a violation of a law.
Under what circumstances does a deviant label transition from primary to secondary deviance?
Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance? The size of a groups does not effect how it operates or what sort of relationships are possible within it because group dynamics are the same regardless of the group size.
What do you understand by secondary group?
Definition of secondary group : a social group characterized by conscious collective interest and formal association. — contrasted with primary group. — compare gesellschaft.
What is labeling theory in sociology?
This refers to a theory of social behaviour which states that the behaviour of human beings is influenced significantly by the way other members in society label them. It has been used to explain a variety of social behaviour among groups, including deviant criminal behaviour.
What is the function of secondary group?
Secondary groups are often larger and impersonal. They may also be task-focused and time-limited. These groups serve an instrumental function rather than an expressive one, meaning that their role is more goal- or task-oriented than emotional. One’s fellow students or coworkers can be examples of a secondary group.
What are secondary groups explain its characteristics?
Main characteristics of secondary group are: (i) Formal and Impersonal Relations (ii) Large in Size (iii) Option of Membership (iv) Active and Inactive Members (v) Relations (vi) Formal Rules (vii) Status of Individual Depends on his Role (viii) Goal Oriented.
What is the importance of secondary group?
Secondary group helps in broadening the outlook of its members. Because it is large in size and its members are widespread. As the secondary group accommodate a large number and variety of individuals and localities this widens the outlook of its members.
What does tertiary deviance mean?
Tertiary deviance. Occurs when a person who has been labeled a deviant seeks to normalize the behavior by relabeling it as nondeviant (when you are labeled by your deviant behavior and it becomes your master status).
What are the concepts of Labelling theory?
Definition. Labeling theory is an approach in the sociology of deviance that focuses on the ways in which the agents of social control attach stigmatizing stereotypes to particular groups, and the ways in which the stigmatized change their behavior once labeled.
What is the difference between positive and negative deviance?
Deviance may be either positive or negative. Negative deviance involves behavior that fails to meet accepted norms. People expressing negative deviance either reject the norms, misinterpret the norms, or are unaware of the norms. Positive deviance involves overconformity to norms.
What is the pluralistic theory?
Classical pluralism is the view that politics and decision-making are located mostly in the framework of government, but that many non-governmental groups use their resources to exert influence. …