Secondary generalized seizures begin in one part of the brain, but then spread to both sides of the brain. In other words, the person first has a focal seizure, followed by a generalized seizure.
- What are secondary causes of seizures?
- What is partial seizure with secondary generalization?
- What are the 2 main types of seizures?
- What are the 3 types of seizures?
- What are the 6 types of seizures?
- What are the 4 types of seizures?
- What are the 12 types of seizures?
- What are the six types of generalized seizures?
- What is a mini seizure?
- What is a Status seizure?
- What is a focal or partial seizure?
- What is the difference between generalized and partial seizures?
- What is a bilateral seizure?
- What is the difference between clonic and myoclonic seizures?
- How serious is a grand mal seizure?
- What is a myoclonic seizure?
- What are the 4 stages of most generalized seizures?
- What is the difference between a grand mal seizure and a regular seizure?
- What is the difference between grand mal and petit mal seizure?
- Does an EEG show past seizures?
- What is a seizure cluster?
- What is considered a long seizure?
- What is the difference between a tonic clonic seizure and status epilepticus?
- What is a partial seizure called?
- What does a partial seizure look like?
- Which type of seizure originates on both side of the brain?
What are secondary causes of seizures?
- Febrile Seizure (under age 5 years)
- Idiopathic.
- Congenital.
- Birth Injury.
- Head Trauma (including due to Child Abuse)
- Gastroenteritis (Rotavirus, Shigella)
- Metabolic disorder. Hypoglycemia. Hyponatremia (most common cause in afebrile children under age 2 years)
What is partial seizure with secondary generalization?
Secondary generalization occurs when partial seizures spread to both sides of the brain, which results in tonic-clonic seizures and loss of consciousness.
What are the 2 main types of seizures?
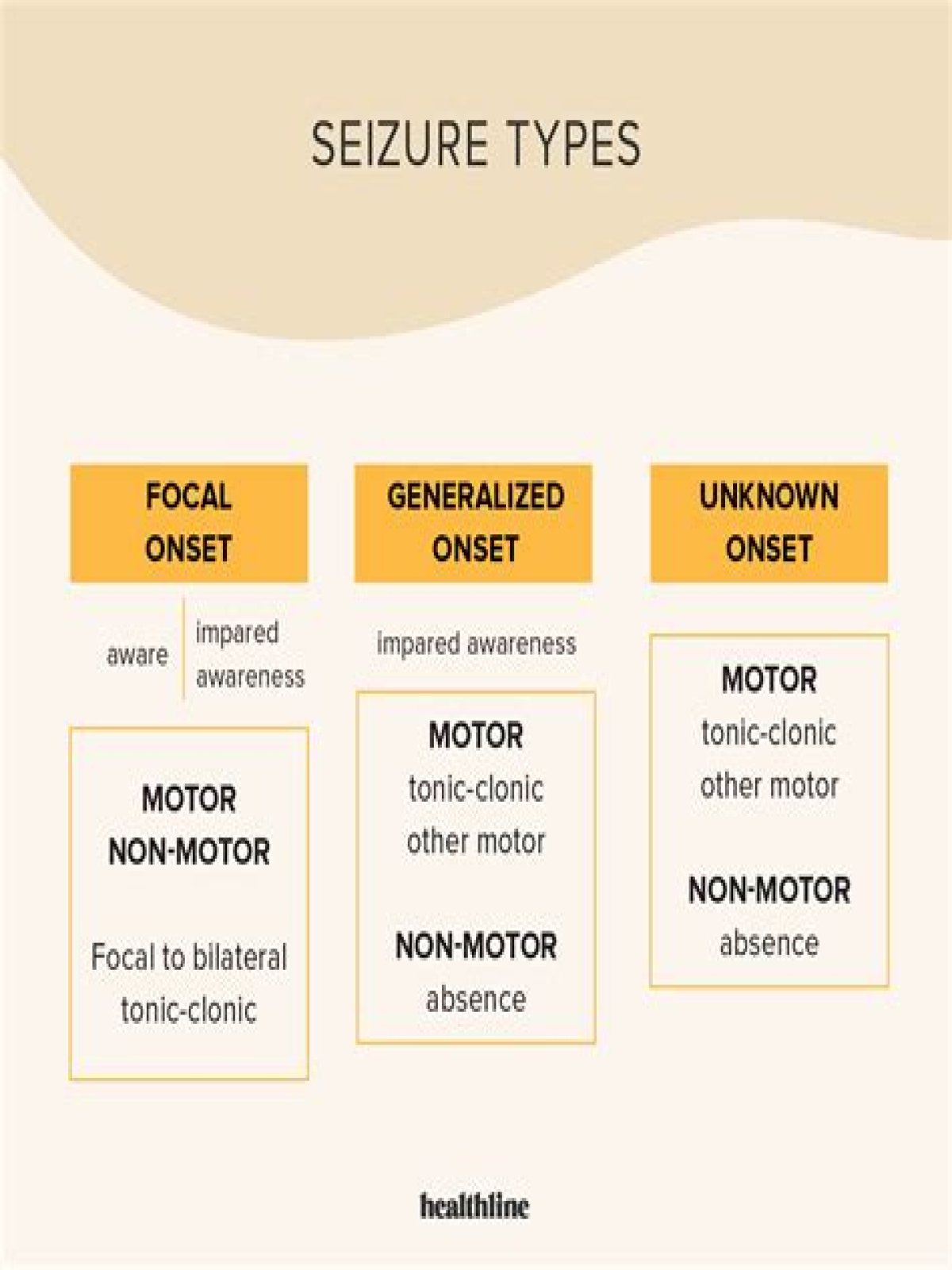
There are two major classes or groups of seizures: focal onset and generalized onset. Focal onset seizures start in one area and can spread across the brain and cause mild or severe symptoms, depending on how the electrical discharges spread.What are the 3 types of seizures?
- Generalized onset seizures:
- Focal onset seizures:
- Unknown onset seizures:
What are the 6 types of seizures?
- Simple Focal Seizures. Simple focal seizures occur for a short amount of time – typically lasting less than one minute. …
- Complex Focal Seizure. …
- Absence Seizure. …
- Atonic Seizure. …
- Tonic-Clonic Seizure. …
- Myoclonic Seizure.
What are the 4 types of seizures?
It causes seizures, which are bursts of electricity in the brain. There are four main types of epilepsy: focal, generalized, combination focal and generalized, and unknown. A person’s seizure type determines what kind of epilepsy they have. Different types of seizures affect the brain in different ways.
What are the 12 types of seizures?
- generalized tonic-clonic seizures (GTC)
- tonic seizures.
- clonic seizures.
- absence seizures.
- myoclonic seizures.
- atonic seizures.
- infantile or epileptic spasms.
What are the six types of generalized seizures?
Generalized seizures include absence, atonic, tonic, clonic, tonic-clonic, myoclonic, and febrile seizures. Loss of consciousness may be accompanied by spasms, stiffening, shaking, muscle contractions or loss of muscle tone.
What is the most common type of seizure?The most common type of seizure is the complex partial seizure. This is a seizure that begins in one part of the brain and then spreads to other regions of the brain.
Article first time published onWhat is a mini seizure?
Overview. A partial (focal) seizure happens when unusual electrical activity affects a small area of the brain. When the seizure does not affect awareness, it is known as a simple partial seizure.
What is a Status seizure?
A seizure that lasts longer than 5 minutes, or having more than 1 seizure within a 5 minutes period, without returning to a normal level of consciousness between episodes is called status epilepticus. This is a medical emergency that may lead to permanent brain damage or death.
What is a focal or partial seizure?
Partial (focal) seizures occur when this electrical activity remains in a limited area of the brain. The seizures can sometimes turn into generalized seizures, which affect the whole brain. This is called secondary generalization.
What is the difference between generalized and partial seizures?
Generalized seizures are produced by electrical impulses from throughout the entire brain, whereas partial seizures are produced (at least initially) by electrical impulses in a relatively small part of the brain. The part of the brain generating the seizures is sometimes called the focus.
What is a bilateral seizure?
A seizure that starts in one area of the brain, then spreads to both sides of the brain as a tonic-clonic seizure is called a focal to bilateral tonic-clonic seizure. This term replaces secondarily generalized seizure. They usually last 1 to 3 minutes, but it may take a longer for a person to recover.
What is the difference between clonic and myoclonic seizures?
The distinction between myoclonic seizures and clonic seizures is not clear. Classically, clonic seizures are rapid rhythmically recurrent events, whereas myoclonic seizures are single or irregularly recurrent events. Mechanisms are different from those of the clonic phase of generalized tonic-clonic seizures.
How serious is a grand mal seizure?
Grand mal seizures can be life threatening. Seek immediate medical care (call 911) for any seizure, as prompt medical treatment may reduce the risk and severity of future seizures.
What is a myoclonic seizure?
Myoclonic seizures are characterized by brief, jerking spasms of a muscle or muscle group. They often occur with atonic seizures, which cause sudden muscle limpness.
What are the 4 stages of most generalized seizures?
In addition to these categorizations, there are four distinct phases of seizures: prodromal, early ictal (the “aura”), ictal, and post-ictal.
What is the difference between a grand mal seizure and a regular seizure?
A grand mal seizure causes a loss of consciousness and violent muscle contractions. It’s the type of seizure most people picture when they think about seizures. A grand mal seizure — also known as a generalized tonic-clonic seizure — is caused by abnormal electrical activity throughout the brain.
What is the difference between grand mal and petit mal seizure?
Generalized Seizures Generalized seizures occur when there is widespread seizure activity in the left and right hemispheres of the brain. The different types of generalized seizures are: absence seizures (formerly known as petit mal) tonic-clonic or convulsive seizures (formerly known as grand mal)
Does an EEG show past seizures?
The EEG generally records brain waves between seizures, called interictal brain waves. These waves may or may not show evidence of seizure activity.
What is a seizure cluster?
Seizure clusters are periods of increased seizure activity, which is having two or more seizures in a 24-hour period. They are disruptive events that can leave you feeling worried, frustrated, or helpless.
What is considered a long seizure?
Most seizures last from 30 seconds to two minutes. A seizure that lasts longer than five minutes is a medical emergency.
What is the difference between a tonic clonic seizure and status epilepticus?
Most tonic-clonic seizures end normally in 1 to 2 minutes, but they may have post-ictal (or after-effects) symptoms for much longer. This makes it hard to tell when a seizure begins and ends. Status epilepticus occurs when…. The active part of a tonic-clonic seizure lasts 5 minutes or longer.
What is a partial seizure called?
Focal seizures, also called partial seizures, occur when there is a disruption of electrical impulses in one part of the brain. A person may be aware that they are having a seizure, in this case, a simple focal seizure, or they may not be aware, which is a complex focal seizure.
What does a partial seizure look like?
changes in how something might taste, feel, look, or sound. distorted vision of items around you or of your own body. smelling an odd odor. tingling sensation in parts of your body, usually the arms or legs.
Which type of seizure originates on both side of the brain?
Tonic and Clonic Seizures: Partial or Generalized A seizure that originates in both halves (hemispheres) of the brain simultaneously, causing stiffness or twitching throughout the body, is known as a generalized tonic or clonic seizure.