So, how does a Hall effect sensor work? Using semiconductors (such as silicon), Hall effect sensors work by measuring the changing voltage when the device is placed in a magnetic field. In other words, once a Hall effect sensor detects that it is now in a magnetic field, it is able to sense the position of objects.
- How does a magnetic sensor work?
- What is a magnetic position sensor?
- What is a magnetic induction sensor and how does it work?
- How does direction sensor work?
- How do you test a sensor?
- How is a magnetic sensor tested for resistance?
- How does a Hall effect sensor work and how is it different from a magnetic sensor?
- How do magnetic sensors obtain information?
- Which sensor is used for direction?
- How do wind direction sensors work?
- For what purpose magnetic compass is used?
- What is hole effect?
- What are symptoms of a bad speed sensor?
- How does eddy current sensor work?
- How do you troubleshoot a sensor?
- How can you tell if the sensor is bad?
- How does a Hall effect rotary position sensor work?
- What is the principle of Hall effect?
- How do we produce magnetic field in Hall effect experiment?
- How many wires does a Hall effect sensor have?
- How does a RPM sensor work?
- Where are magnetic field sensors used?
- What is the sensing range for magnetic proximity sensors?
- What is the function of magnetic switch?
- What are some of the common uses of position sensors?
- Where is position sensor used?
- How many types of position sensors are there?
- Why does the anemometer spin?
- What is a weathercock used for?
How does a magnetic sensor work?
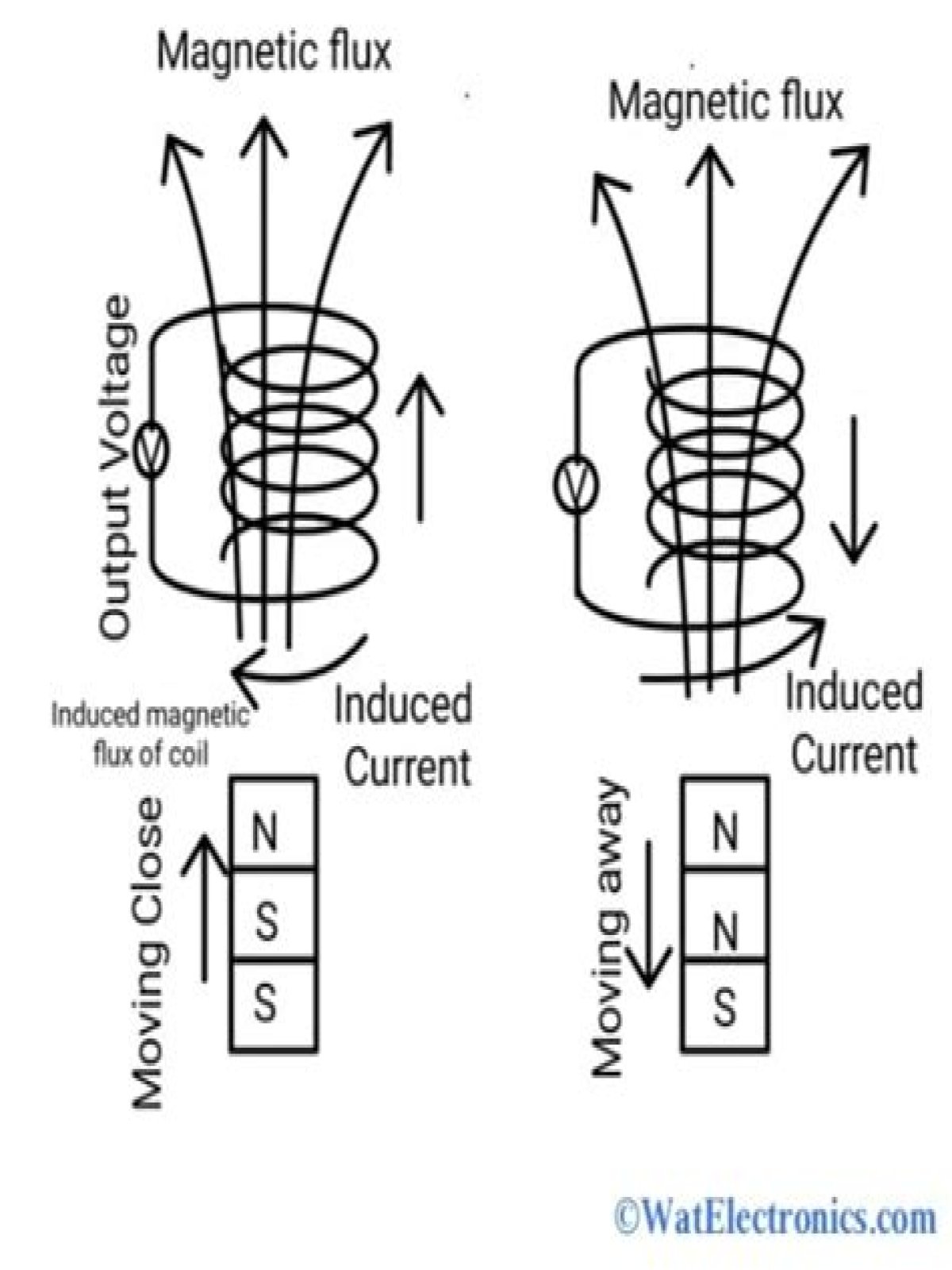
Magnetic sensors detect moving ferrous metal. The simplest magnetic sensor consists of a wire coiled around a permanent magnet. A ferrous object approaching the sensor changes magnetic flux through the coil, generating a voltage at the coil terminals. … of target travel and can sense very small ferrous objects.
What is a magnetic position sensor?
Respond to the presence or to the interruption of a magnetic field. Measure linear, angular, or rotary movement of magnet attached to moving object. Precise Position Performance.
What is a magnetic induction sensor and how does it work?
Inductive sensors use currents induced by magnetic fields to detect nearby metal objects. The inductive sensor uses a coil (an inductor) to generate a high frequency magnetic field as shown in Figure 1 below. If there is a metal object near the changing magnetic field, current will flow in the object.How does direction sensor work?
The wind direction sensor is a physical device that measures and transmits wind direction information. It works through the rotation of a wind vane arrow and transmits its measurement information to the coaxial encoder board, and at the same time outputs the relevant value of the wind direction.
How do you test a sensor?
- Locate the sensor. …
- Check the sensor for loose connections or worn insulation.
- Set a digital volt ohm meter to measure 20 kilo Ohms.
- Attach the DVOM’s positive lead to the central terminal of the sensor and the negative to one of the remaining terminals.
How is a magnetic sensor tested for resistance?
Steps for Permanent Magnet Sensor Testing Measure the resistance of the sensor across the two pins. … Place the meter leads across the sensor and measure the AC voltage output. Typically, if the shaft is rotated at about one turn every 2 seconds the output should be around .
How does a Hall effect sensor work and how is it different from a magnetic sensor?
Magnetic sensors are used to change electrical signals after detecting a magnetic state. … A Hall sensor detects the strength of a magnetic field perpendicular to it, whereas an MR sensor detects the angle of a parallel magnetic field.How do magnetic sensors obtain information?
Magnetic field sensors either utilize an internal magnet or directly detect a permanent or electromagnetic field. … Hall Switches, Reed Switches, and other external magnet sensors detect the magnetic field from a magnet or electro coil. They also are available in analog and digital versions.
What is magnetic proximity sensor?Magnetic proximity sensors are non-contact proximity device which detects the magnetic objects (e.g. permanent magnets). They sense the presence of a magnetic object.
Article first time published onWhich sensor is used for direction?
The wear-free, magnetic Hall sensors are used for rotation direction detection. The magnetic field which is produced by a permanent magnet is output as a signal according to the direction of rotation.
How do wind direction sensors work?
Wind direction sensor is a kind of physical device that detects and senses the wind direction information. It works by the rotation of the arrow of the wind direction, and transmits it to the coaxial code plate, at the same time outputs the relevant values of the wind direction.
For what purpose magnetic compass is used?
magnetic compass, in navigation or surveying, an instrument for determining direction on the surface of Earth by means of a magnetic pointer that aligns itself with Earth’s magnetic field.
What is hole effect?
Hole effect structures most often indicate a form of cyclicity or periodic-ity, which is a common and legitimate spatial characteristic in geology. Ignoring these non-monotonic structures may result in unrealistic heterogeneity models that do not reproduce the observed patterns of varibility.
What are symptoms of a bad speed sensor?
- Transmission problems. …
- Erratic speedometer readings. …
- Inability to engage cruise control. …
- Lack of torque converter clutch application. …
- Check Engine Light is triggered. …
- An internal electrical fault in the speed sensor. …
- Damage on the sensor itself. …
- Poor vehicle maintenance.
How does eddy current sensor work?
Eddy Current Sensors work in magnetic fields. The driver creates an alternating current in a sensing coil at the end of a probe. The alternating current then creates an alternating magnetic field which induces smaller currents within the target material, these currents are referred to as Eddy Currents.
How do you troubleshoot a sensor?
- 1.) Check Sensor Connection. …
- 2.) Check Gap. …
- 3.) Resistance Measurement (two wire plug only) …
- 4.) Check Power (three wire plug only) …
- 5.) Check Wiring (three wire plug only)
How can you tell if the sensor is bad?
The sensor’s out put can be checked with a voltmeter, or observed on a scan tool. If there are any drops in the output as the throttle opens, the sensor is bad and needs to be replaced. On some older vehicles, the idle voltage setting of the sensor must be adjusted to a specified voltage.
How does a Hall effect rotary position sensor work?
When the operator removes their foot from the pedal, the Hall effect rotary position sensor senses the change in position and sends a signal to the engine to reduce the flow of fuel and air across the throttle plate. The vehicle responds to this signal by slowing down.
What is the principle of Hall effect?
The principle of Hall Effect states that when a current-carrying conductor or a semiconductor is introduced to a perpendicular magnetic field, a voltage can be measured at the right angle to the current path. This effect of obtaining a measurable voltage is known as the Hall Effect.
How do we produce magnetic field in Hall effect experiment?
When electrons flow through a conductor, a magnetic field is produced. Thus, it is possible to create a non-contacting current sensor. The device has three terminals. A sensor voltage is applied across two terminals and the third provides a voltage proportional to the current being sensed.
How many wires does a Hall effect sensor have?
A Hall effect sensor typically has 3 wires. Power, Signal Ground and the Signal Output. A Hall effect sensor produces a consistent digital square wave signal each time a magnet or ferrous metal passes the tip of the sensor, regardless of the speed at which the trigger material.
How does a RPM sensor work?
In principle, RPM sensors convert mechanical motion into electric pulses with or without direct contact when positioned near a turning rotor, gear, shaft or other regularly moving device. The resultant output signals are then fed to a digital counter, totaliser, tachometer, or other monitoring and control device.
Where are magnetic field sensors used?
Magnetic sensors are widely used in a variety of consumer products such as printers, scanners, cameras, and flat panels. One of the fastest growing applications of magnetic sensors is mobile navigation – the electronic compass is a must have feature in mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets.
What is the sensing range for magnetic proximity sensors?
What is the sensing range for magnetic proximity sensors? Explanation: Magnetic proximity sensors have no electrical noise effect and it can work on DC, AC, AC/DC. These types of sensors have highest sensing range upto 120mm.
What is the function of magnetic switch?
Simple magnetic switches are used to detect the opening of doors and windows. A basic magnetic switch comprises two parts— the magnet and a magnetically sensitive switch (usually a reed switch enclosed within a glass envelope). Switches may be either normally open (close on alarm) or normally closed (open on alarm).
What are some of the common uses of position sensors?
- Medical equipments.
- Packaging machines.
- Injection molding machines.
- Bullet trains taking round curves.
- Drive-by-wire cars.
- Fly-by-wire aircraft systems.
Where is position sensor used?
Position sensors are used in many applications, they are used across industries such as; automotive, motorsport, medical, agriculture, robotics, industrial processing, mobile vehicle, test and lab applications, food & beverage, packaging, machine tool, wrapping and many more.
How many types of position sensors are there?
There are two different types of position sensor based on the measurement being taken; linear or rotary. Linear position sensors are used for linear motions; up, down or side to side. Rotary position sensors are for measuring turning movements, either linear or rotary.
Why does the anemometer spin?
Air is made up of tiny molecules. When molecules are heated, they move faster. … This movement of air from a higher pressure area to a relatively lower pressure area is what generates wind. When wind pushes the cups on the anemometer, they spin around the central axis.
What is a weathercock used for?
A wind vane, weather vane, or weathercock is an instrument used for showing the direction of the wind. It is typically used as an architectural ornament to the highest point of a building.