Effective Clustered Indexes can often improve the performance of many operations on a SQL Server table. … To be clear, having a non-clustered index along with the clustered index on the same columns will degrade performance of updates, inserts, and deletes, and it will take additional space on the disk.
- What is the advantage of clustered index?
- Should you always have a clustered index?
- What is the main difference between clustered and nonclustered index?
- Why use a non-clustered index?
- What is nonclustered index?
- Why non-clustered index is slower?
- What is nonclustered index in SQL?
- Can a table have both clustered and nonclustered index?
- What is the difference between dense and sparse index?
- Is primary key clustered index?
- Can we create primary key without clustered index?
- Can clustered index have multiple columns?
- Can we create clustered index on non unique column?
- Does nonclustered index allow duplicates?
- How many clustered and nonclustered index can be applied to a table?
- How do I get rid of a non clustered index?
- Does indexing improve performance?
- Why many indexes are not good for performance?
- Is indexing good or bad?
- What is B tree index?
- What is the function of the Except operation?
- Which one is true about the clustered index?
- What is the advantage of sparse index over dense index?
- What are the advantages of dense indexing and sparse indexing?
- When it is preferable to use a dense index rather than a sparse index explain?
- What is difference between primary key and clustered index?
- What is primary key nonclustered?
- What does PK mean in database?
- Can clustered index have null value?
What is the advantage of clustered index?
A clustered index is useful for range queries because the data is logically sorted on the key. You can move a table to another filegroup by recreating the clustered index on a different filegroup. You do not have to drop the table as you would to move a heap.
Should you always have a clustered index?
As a rule of thumb, every table should have a clustered index. Generally, but not always, the clustered index should be on a column that monotonically increases–such as an identity column, or some other column where the value is increasing–and is unique. … With few exceptions, every table should have a clustered index.
What is the main difference between clustered and nonclustered index?
A Clustered index is a type of index in which table records are physically reordered to match the index. A Non-Clustered index is a special type of index in which logical order of index does not match physical stored order of the rows on disk.Why use a non-clustered index?
Advantages of Non-clustered index A non-clustering index helps you to retrieves data quickly from the database table. Helps you to avoid the overhead cost associated with the clustered index. A table may have multiple non-clustered indexes in RDBMS. So, it can be used to create more than one index.
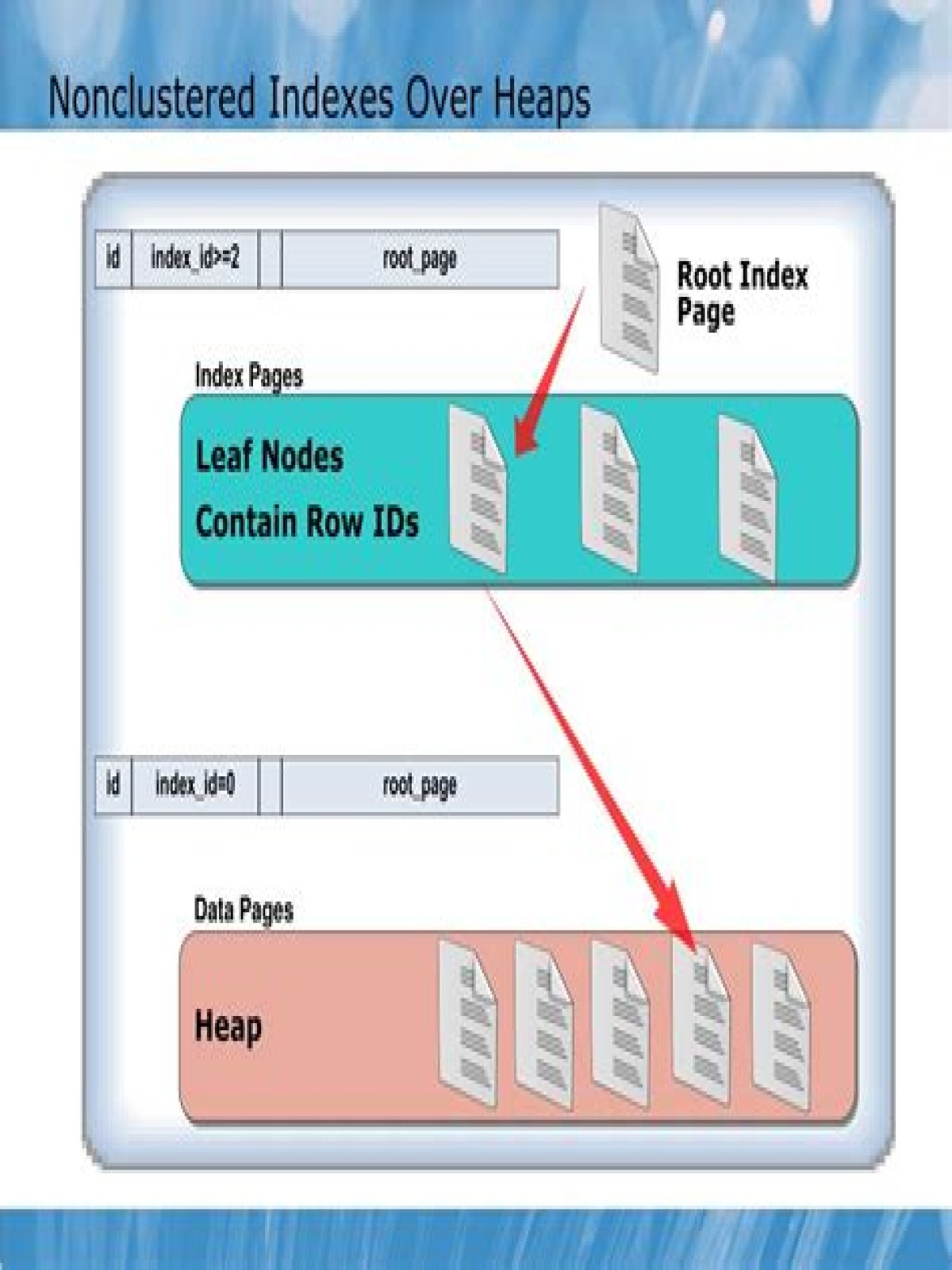
What is nonclustered index?
A non-clustered index (or regular b-tree index) is an index where the order of the rows does not match the physical order of the actual data. … In a non-clustered index, the leaf pages of the index do not contain any actual data, but instead contain pointers to the actual data.
Why non-clustered index is slower?
Therefore when we query for data, first the non-clustered index is searched to get the address of the data and then the lookup is performed on the clustered index to get the data. Hence this makes the non-clustered index usually slower than the clustered index. There can be multiple non-clustered indexes in a table.
What is nonclustered index in SQL?
You can create nonclustered indexes in SQL Server by using SQL Server Management Studio or Transact-SQL. A nonclustered index is an index structure separate from the data stored in a table that reorders one or more selected columns.Can a table have both clustered and nonclustered index?
Both clustered and nonclustered indexes can be unique. This means no two rows can have the same value for the index key. Otherwise, the index is not unique and multiple rows can share the same key value.
What is the advantage of the clustered index Mcq?1.It is fast to update the records. 2.It does not need extra work for SQL queries. 3.It minimizes the page transfer and maximizes the cache hits.
Article first time published onWhat is the difference between dense and sparse index?
Dense indices are faster in general, but sparse indices require less space and impose less maintenance for insertions and deletions.
Is primary key clustered index?
The primary key is the default clustered index in SQL Server and MySQL. This implies a ‘clustered index penalty’ on all non-clustered indexes.
Can we create primary key without clustered index?
Can I have a primary key without clustered index? Yes. As you mentioned, a primary key constraint is backed by a clustered index by default.
Can clustered index have multiple columns?
This results in wonderful performance—when you only have to worry about one particular column. But what if you want to order the data by more than one column? You can’t use a clustered index, but you can create an unclustered index on multiple columns and gain a nice performance increase.
Can we create clustered index on non unique column?
So, when you create the clustered index – it must be unique. But, SQL Server doesn’t require that your clustering key is created on a unique column. You can create it on any column(s) you’d like. Internally, if the clustering key is not unique then SQL Server will “uniquify” it by adding a 4-byte integer to the data.
Does nonclustered index allow duplicates?
Unique Non Cluster Index only accepts unique values. It does not accept duplicate values. After creating a unique Non Cluster Index, we cannot insert duplicate values in the table.
How many clustered and nonclustered index can be applied to a table?
There can be only one clustered index per table. However, you can create multiple non-clustered indexes on a single table.
How do I get rid of a non clustered index?
To drop a clustered or nonclustered index, issue a DROP INDEX command. When you do this, the metadata, statistics, and index pages are removed. If you drop a clustered index, the table will become a heap. Once an index has been dropped, it can’t be rebuilt – it must be created again.
Does indexing improve performance?
Effective indexes are one of the best ways to improve performance in a database application. … By using the index in the back of a book, a reader can complete the task in a much shorter time. In database terms, a table scan happens when there is no index available to help a query.
Why many indexes are not good for performance?
The reason that having to many indexes is a bad thing is that it dramatically increases the amount of writing that needs to be done to the table. … In addition to that, write changes have to then be made to all 10 data pages (one data page per index) so that the data can be written to the data file as well.
Is indexing good or bad?
Disadvantages of using indexes As noted above, wrong indexes can significantly slow down SQL Server performance. But even the indexes that provide better performance for some operations, can add overhead for others. … Another cost of having indexes on tables is that more data pages and memory is used.
What is B tree index?
A B-tree index creates a multi-level tree structure that breaks a database down into fixed-size blocks or pages. Each level of this tree can be used to link those pages via an address location, allowing one page (known as a node, or internal page) to refer to another with leaf pages at the lowest level.
What is the function of the Except operation?
3. What is the function of the except operation? Explanation: The except operation includes the results of the first query but excludes the results of the second query. It automatically eliminates duplicates but if we want to retain duplicates we must use except all in place of except.
Which one is true about the clustered index?
Que.Which one is true about clustered index?b.Clustered index is built by default on unique key columnsc.Clustered index is not built on unique key columnsd.None of the mentionedAnswer:Clustered index is built by default on unique key columns
What is the advantage of sparse index over dense index?
Sparse indexing has two advantages. The primary one is that it reduces the size of the index, saving space and decreasing maintenance of the index. By decreasing the size of the index, performance is improved. The second advantage is that you do not need to generate unnecessary index entries.
What are the advantages of dense indexing and sparse indexing?
In a dense index, a record is created for every search key valued in the database. A sparse indexing method helps you to resolve the issues of dense Indexing. The secondary Index in DBMS is an indexing method whose search key specifies an order different from the sequential order of the file.
When it is preferable to use a dense index rather than a sparse index explain?
Answer: It is preferable to use a dense index instead of a sparse index when the file is not sorted on the indexed field (such as when the index is a secondary index) or when the index file is small compared to the size of memory.
What is difference between primary key and clustered index?
And a primary key is a piece of data that uniquely identifies that data. An index on the other hand is something that describes a (faster) way to access data. … In SQL Server specifically, a clustered index is an index that dictates the physical order of storage of the rows.
What is primary key nonclustered?
Nonclustered primary key constraints are nonclustered indexes behind the scenes. A nonclustered primary key may be created on a heap, or a table with a clustered index. Antipattern: sometimes people create a clustered index and a non-clustered primary key on the same column or columns.
What does PK mean in database?
Primary Key Constraints A table typically has a column or combination of columns that contain values that uniquely identify each row in the table. This column, or columns, is called the primary key (PK) of the table and enforces the entity integrity of the table.
Can clustered index have null value?
For the clustered index, the column doesn’t need to be unique and/or without null. A column with duplicates and null values is fine for creating a clustered index. For a foreign key, it must reference a column with a unique index on it but not necessarily a primary key or without null value.