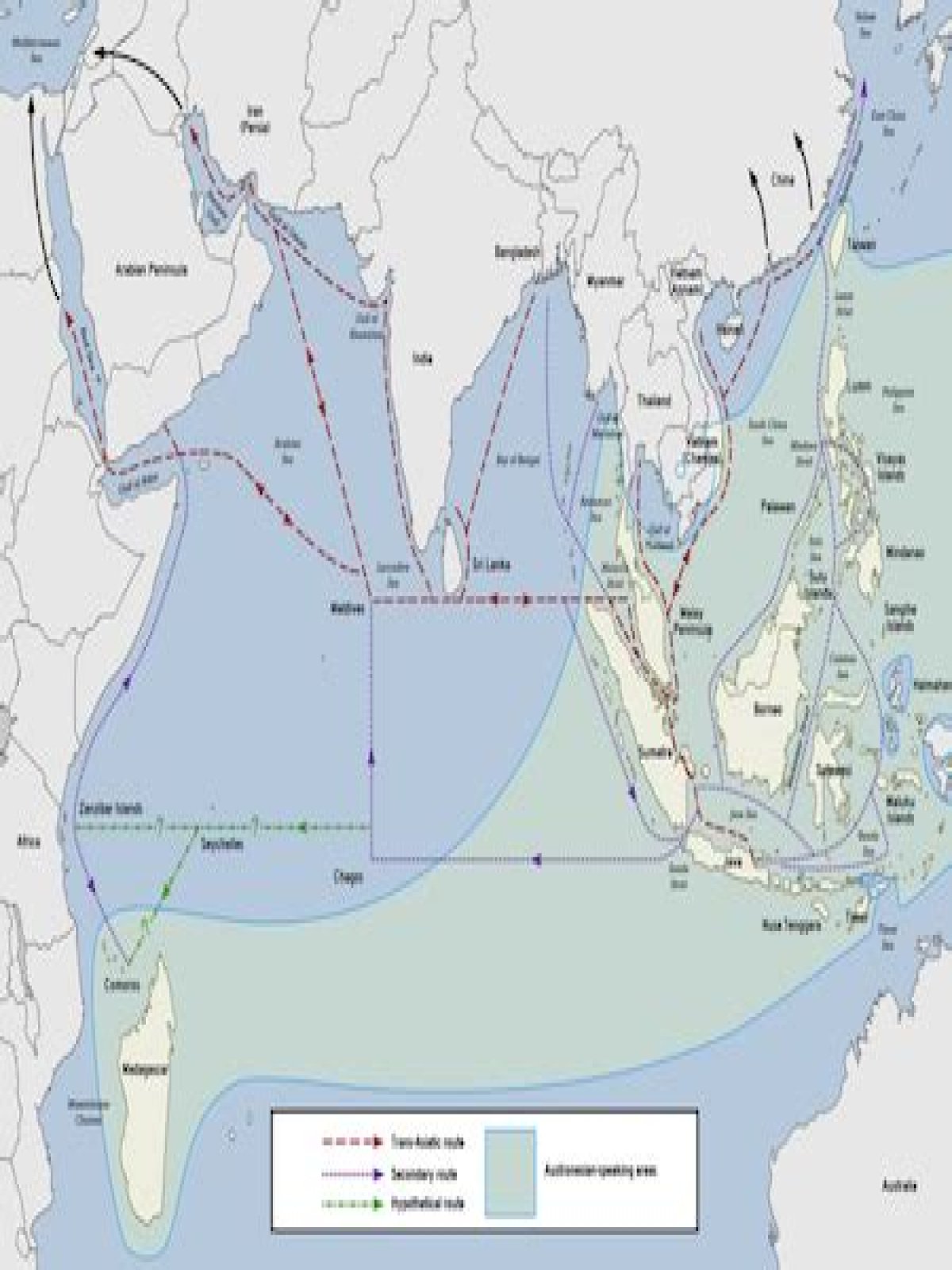
The Indian Ocean trade routes connected Southeast Asia, India, Arabia, and East Africa, beginning at least as early as the third century BCE. … Domestication of the camel helped bring coastal trade goods such as silk, porcelain, spices, incense, and ivory to inland empires, as well. Enslaved people were also traded.
- What were some goods traded along the Indian Ocean?
- Why was the Indian Ocean trade important?
- What was traded on the trade routes?
- How was trade different on the Indian Ocean from the Silk Road?
- What are the main inland trade routes of ancient time?
- What were the three trade routes?
- What are some of the reasons the Indian Ocean trade took off and was so popular?
- Who made and helped develop the Indian Ocean trade routes?
- What was traded on the Silk Road?
- Which was the main trade Centre on the trade route between India and Europe since ancient times?
- Why was salt traded on the Silk Road?
- What was the most famous trade route?
- What were the most important trade routes?
- What was one of the most important goods traded on the ancient north and south trade routes?
- Why did many trade routes cross the Mediterranean Sea?
- What is the Indian Ocean trade quizlet?
- What did India trade on the Silk Road?
- Who traded on the Silk Road?
- What did Baghdad trade on the Silk Road?
- Which trade route was most profitable during the Mauryan period?
- Which were the two major trade routes of the medieval period?
- What was traded in ancient times?
- Where was salt traded on the Silk Road?
- Who bought salt on the Silk Road?
- How was salt traded?
What were some goods traded along the Indian Ocean?
Petroleum dominates commerce, as the Indian Ocean has come to be an important throughway for transport of crude oil to Europe, North America, and East Asia. Other major commodities include iron, coal, rubber, and tea.
Why was the Indian Ocean trade important?
The Indian Ocean is home to major sea routes connecting the Middle East, Africa and East Asia with Europe and the Americas. These vital sea routes (i) facilitate maritime trade in the Indian Ocean region, (ii) carry more than half of the world’s sea-borne oil,3 and (iii) host 23 of the world’s top 100 container ports.
What was traded on the trade routes?
Gold, slaves, salt, and cloth were traded along the route, as were objects like ostrich feathers and European guns. The trade route was instrumental in the spread of Islam from the Berbers in North Africa into West Africa, and with Islam came Arabic knowledge, education, and language.How was trade different on the Indian Ocean from the Silk Road?
Although they were both trade routes, the Indian Ocean sea lanes traded overseas and the Eurasian Silk Roads were land routes. Indian Ocean sea lanes connect Southeast Asia, India, Arabia, and East Africa. The Eurasian Silk Roads connected East and West China to the Mediterranean.
What are the main inland trade routes of ancient time?
The Silk Road may be the most famous ancient trade route. This route connected China and the ancient Roman Empire, and people traded silk along this pathway. In exchange for the silk, the Chinese got gold, silver, and wool from Europe.
What were the three trade routes?
The three trade routes used during the Hellenistic era are mentioned below: – The ptolemaic empire, The Antigonid empire and the seleucid empire in Egypt, Macedonia and in Persia and Mesopotamia were three hellenic empires that followed Alexander death. – From the war of succession these three empires emerged.
What are some of the reasons the Indian Ocean trade took off and was so popular?
What are some of the reasons the Indian Ocean Trade took off and was so popular? They were seasonal and consistent. Monsoons would help carry ships from Africa to India between April and September. They carried ships back from November to February.Who made and helped develop the Indian Ocean trade routes?
The Portuguese under Vasco da Gama discovered a naval route to the Indian Ocean through the southern tip of Africa in 1497–98. Initially, the Portuguese were mainly active in Calicut, but the northern region of Gujarat was even more important for trade, and an essential intermediary in east–west trade.
How did trade in the Indian Ocean lead to political change?Trade stimulated political change as ambitious rulers use well derived from commerce to construct larger and more centrally governed states or cities; experienced cultural change as local people were attracted to foreign religious ideas from Hindu, Buddhist, or Islamic sources.
Article first time published onWhat was traded on the Silk Road?
The silk road was a network of paths connecting civilizations in the East and West that was well traveled for approximately 1,400 years. … They traded goods such as silk, spices, tea, ivory, cotton, wool, precious metals, and ideas.
Which was the main trade Centre on the trade route between India and Europe since ancient times?
The main trade Center on the trade route between India and Europe since ancient times is The Silk Road. The route is over 6,500 km long and got it’s name because the early Chinese traded silk along it.
Why was salt traded on the Silk Road?
“The ancient Qanat-Karez provided surge flooding for short periods to desalinate the soil of the Sabkha basin,” Bloch said. The leached salt formed a microbial, layered crust, allowing for the production of purified salt along the Middle Eastern section of the Silk Road.
What was the most famous trade route?
SILK ROAD // THE MOST FAMOUS TRADE ROUTE IN THE WORLD The Silk Road is the most famous ancient trade route, linking the major ancient civilizations of China and the Roman Empire. Silk was traded from China to the Roman empire starting in the first century BCE, in exchange for wool, silver, and gold coming from Europe.
What were the most important trade routes?
- Silk Road. The Silk Road is the world’s most famous trade route, starting from China, passing through Anatolia and Asia and reaching Europe. …
- Spice Route. …
- Royal Road. …
- Incense Route. …
- The Tea Horse Road. …
- The Salt Route.
What was one of the most important goods traded on the ancient north and south trade routes?
What did they trade? The main items traded were gold and salt. The gold mines of West Africa provided great wealth to West African Empires such as Ghana and Mali. Other items that were commonly traded included ivory, kola nuts, cloth, slaves, metal goods, and beads.
Why did many trade routes cross the Mediterranean Sea?
The Mediterranean sea lanes connect the people, empires and civilizations of North Africa, Asia, and Europe through trade. … Although trade routes were designed for the exchange of goods and materials they became a way to share religion, ideas, languages, art, science, and technology.
What is the Indian Ocean trade quizlet?
-the indian ocean trade network were trade routes on the indian ocean. … -People would use these routes for bulk trading. -people got there by being guided my monsoons.
What did India trade on the Silk Road?
India was famous for its fabrics, spices and semi-precious stones, dyes, and ivory. … Eastern Europe imported rice, cotton, woolen and silk fabrics from Central Asia and exported considerable volumes of skins, furs, fur animals, bark for skin processing, cattle and slaves to Khoresm.
Who traded on the Silk Road?
Silk Road, also called Silk Route, ancient trade route, linking China with the West, that carried goods and ideas between the two great civilizations of Rome and China. Silk went westward, and wools, gold, and silver went east. China also received Nestorian Christianity and Buddhism (from India) via the Silk Road.
What did Baghdad trade on the Silk Road?
Goods that passed through the city included diamonds, soap, ivory, camel fur, honey etc. Items were often traded in Baghdad and then re-exported, along with locally manufactured goods. Local products included silk, textiles, glass, paper and Qashani tiles.
Which trade route was most profitable during the Mauryan period?
Trade depended upon its routes, which presented a problem for a continent like India. Grand Trunk Road: The Greeks tell of the Royal Road leading from the North West Frontier to Pataliputra, the Grand Trunk Road of those days, with a length of 10,000 stadia = about 13,000 miles (Strabo XV. 1, 11).
Which were the two major trade routes of the medieval period?
The Silk Route and Spice Route were the two major trade routes during the medieval period.
What was traded in ancient times?
Early trade largely focused on luxury goods like precious metals, spices, and fine textiles, but eventually, as transportation by ship became faster, more reliable, and cheaper, even mundane items like olives and fish paste were exported across great distances.
Where was salt traded on the Silk Road?
Camel caravans from North Africa carried bars of salt as well as cloth, tobacco, and metal tools across the Sahara to trading centers like Djenne and Timbuktu on the Niger River. Some items for which the salt was traded include gold, ivory, slaves, skins, kola nuts, pepper, and sugar.
Who bought salt on the Silk Road?
The West Africans got their salt and the Muslim traders got gold in return so they could buy stuff traded on the Mediterranean Sea. Just like with the Silk Road, eventually other goods besides gold and salt were traded.
How was salt traded?
Transported via camel caravans and by boat along such rivers as the Niger and Senegal, salt found its way to trading centres like Koumbi Saleh, Niani, and Timbuktu, where it was either passed further south or exchanged for other goods such as ivory, hides, copper, iron, and cereals.