But the frequency remains the same. But wavelength and velocity are inversely proportional to each other. So, when the wavelength changes, the frequency should also change.
- What happens to wavelength when refracted?
- What happens to the wavelength of light if the index of refraction increases?
- What happens to wavelength and frequency during refraction?
- What happens when light is refracted by matter?
- What is the relationship between the wavelength of light and the angle of refraction?
- Why does wavelength decrease when frequency increases?
- What happens to the wavelength of light as it goes from air to water?
- Does light change wavelength in glass?
- How does the index of refraction depend on the wavelength of light?
- What is refractive index Does it depend on the wavelength of light?
- How is wavelength related to refraction of a specific color of light?
- When light is refracted into a denser medium?
- When light travels from rarer to denser medium the wavelength decreases?
- What happens to the reflected and refracted rays as you change the angle of the incident light beam?
- When wavelength decreases what happens to the frequency?
- What happens to the wavelength and frequency of the electromagnetic waves as it progresses from left to right?
- What is the relationship of wavelength of frequency?
- What happens when light hits a glass block at an angle?
- What happens to the velocity of light its wavelength and frequency?
- What happens when light travels from air to glass?
- When light is refracted from air into glass the wavelength decreases?
- When a light wave enters a new medium and is refracted?
- How is a wave refracted?
- What is the wavelength of light in air?
- What happens to the wavelength and frequency of the light waves as they enter water from air?
- What happens to the direction of the light wave?
- How can wavelength change without changing frequency?
- Is wavelength inversely proportional to frequency?
- Is wavelength of light constant?
What happens to wavelength when refracted?
The bending of light as it passes from one medium to another is called refraction. … The amount of refraction increases as the wavelength of light decreases. Shorter wavelengths of light (violet and blue) are slowed more and consequently experience more bending than do the longer wavelengths (orange and red).
What happens to the wavelength of light if the index of refraction increases?
v is the velocity of light in the medium. λ is the wavelength. Hence refractive index is inversely proportional to wavelength. Implies greater the wavelength lesser the refractive index.
What happens to wavelength and frequency during refraction?
Wave speed, frequency and wavelength in refraction Although the wave slows down, its frequency remains the same, due to the fact that its wavelength is shorter. When waves travel from one medium to another the frequency never changes. … The wave is slower but the wavelength is shorter meaning frequency remains the same.What happens when light is refracted by matter?
Refraction of Light: as it passes from less dense to more dense mediums. When light passes from a less dense to a more dense substance, (for example passing from air into water), the light is refracted (or bent) towards the normal. … The bending occurs because light travels more slowly in a denser medium.
What is the relationship between the wavelength of light and the angle of refraction?
Wavelength and refractive index Remember in the medium where the light is faster (ie bigger speed), the angle is bigger and the wavelength is bigger.
Why does wavelength decrease when frequency increases?
The wavelength is inversely proportional to frequency of the wave. Which means, waves with higher frequencies have shorter wavelengths, and lower frequencies have longer wavelengths.
What happens to the wavelength of light as it goes from air to water?
Light travels as waves, with the wavefronts perpendicular to the direction of motion. … As light moves from air into water, it not only slows, but the wavelength changes. The animation below illustrates how the wavelength becomes shorter in the denser medium of water.Does light change wavelength in glass?
The wavelength of light decreases as it is moving from air to glass. The light ray moves towards the normal. In the Refraction phenomenon, only the frequency that always same. So, the speed an its wavelength will be changed.
Does frequency change when light refracted?But the frequency remains the same. But wavelength and velocity are inversely proportional to each other. So, when the wavelength changes, the frequency should also change.
Article first time published onHow does the index of refraction depend on the wavelength of light?
The refractive index varies with wavelength linearly because different wavelengths interfere to different extents with the atoms of the medium. It is important to use monochromatic light to prevent dispersion of light into different colours. The chosen wavelength should not be absorbed by the medium.
What is refractive index Does it depend on the wavelength of light?
Refractive index of a medium decreases with increase in wavelength of light. Refractive index of a medium for violet light (least wavelength) is greater than that for red light (greatest wavelength).
For any substance, as the wavelength of light increases, the refractive index (or the bending of light) decreases. In other words, blue light, which comprises the shortest wavelength region in visible light, is refracted at significantly greater angles than is red light, which has the longest wavelengths.
When light is refracted into a denser medium?
its wavelength increases but frequency remains unchanged.
When light travels from rarer to denser medium the wavelength decreases?
As light travels from the rarer to denser medium its speed decreases thus the wavelength also decreases. but the frequency remains the same .
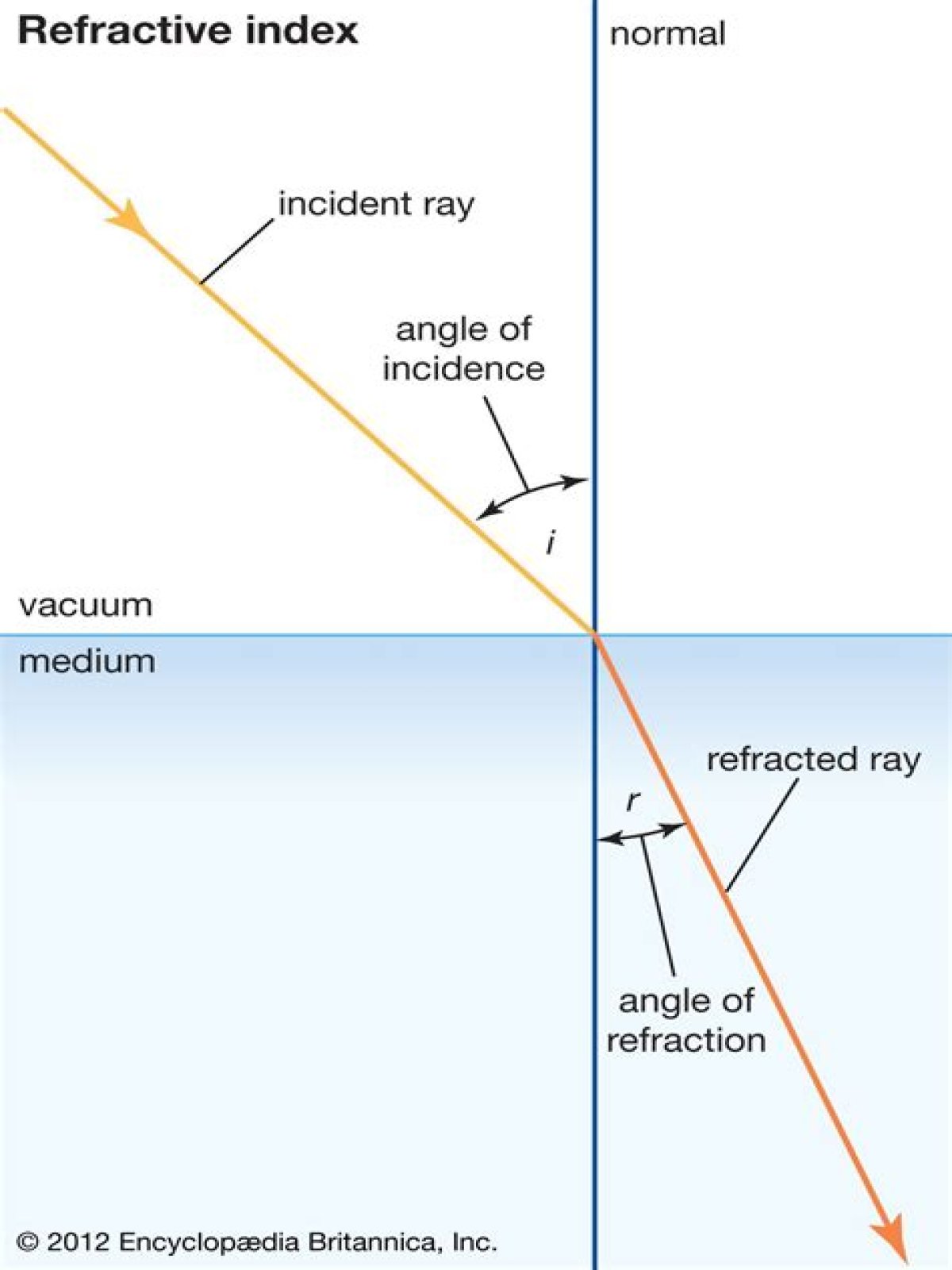
What happens to the reflected and refracted rays as you change the angle of the incident light beam?
What happens to the reflected and refracted rays as you change the angle of the incident light beam? Eventually the refracted ray will make an angle of 90° with the surface normal. If the angle of incidence is increased beyond that angle, then refraction does not occur.
When wavelength decreases what happens to the frequency?
The number of complete wavelengths in a given unit of time is called frequency (f). As a wavelength increases in size, its frequency and energy (E) decrease. From these equations you may realize that as the frequency increases, the wavelength gets shorter. As the frequency decreases, the wavelength gets longer.
What happens to the wavelength and frequency of the electromagnetic waves as it progresses from left to right?
As you go from left → right, the wavelengths get smaller and the frequencies get higher. This is an inverse relationship between wave size and frequency. (As one goes up, the other goes down.)
What is the relationship of wavelength of frequency?
Frequency and wavelength are inversely proportional to each other. The wave with the greatest frequency has the shortest wavelength. Twice the frequency means one-half the wavelength. For this reason, the wavelength ratio is the inverse of the frequency ratio.
What happens when light hits a glass block at an angle?
The light enters the curved face of the block directly, so no refraction is seen here. … At a specific angle, the light ray will no longer leave the block. At this point the angle of incidence is called the critical angle. Any further increase in the angle of incidence will mean the ray is reflected , not refracted.
What happens to the velocity of light its wavelength and frequency?
When light goes from a vacuum to some medium, like water, its speed and wavelength change, but its frequency f remains the same. … This implies that v = fλn, where λn is the wavelength in a medium and that λn=λn λ n = λ n , where λ is the wavelength in vacuum and n is the medium’s index of refraction.
What happens when light travels from air to glass?
When light travels from air into glass, It bends towards the normal line and the light slows down and changes direction slightly. When light travels from a less dense substance to a denser substance, the refracted light bends more towards the normal line.
When light is refracted from air into glass the wavelength decreases?
Its wavelength decrease but frequency remain unchanged.
When a light wave enters a new medium and is refracted?
As the light wave enters a new medium some of the light is reflected, and some is refracted. If the angle of refraction is 90º or higher, the light will only reflect. This is called total internal reflection.
How is a wave refracted?
Refraction is the bending of a wave-front as it travels at different speeds over water of different depths. When different parts of the same wave-front travel at different speeds, the wave bends towards the slower part. The shallower the water, the slower the wave; therefore the wave bends towards the shallower water.
What is the wavelength of light in air?
Given: Wavelength of light in air = λa = 6000 Å = 6000 x 10-10 m = 6 x 10-7 m, Refractive index of medium = μ = 1.6, Velocity of light in air = ca = 3 x 108 m/s.
What happens to the wavelength and frequency of the light waves as they enter water from air?
What happens to the wavelength and frequency of the light waves as they enter water from air? … Wavelength decreases, and frequency will stay the same.
What happens to the direction of the light wave?
Refraction is the bending of the path of a light wave as it passes from one material into another material. … The tendency of a ray of light to bend one direction or another is dependent upon whether the light wave speeds up or slows down upon crossing the boundary.
How can wavelength change without changing frequency?
The colour of light is determined by its frequency according to the electromagnetic spectrum. However, wavelength can change without changing the frequency, for example when it enters a material with a higher refractive index.
Is wavelength inversely proportional to frequency?
Because the velocity is constant, any increase in frequency results in a subsequent decrease in wavelength. Therefore, wavelength and frequency are inversely proportional.
Is wavelength of light constant?
The wavelength of light is not a physical constant … it varies from lightwave to lightwave, and it can vary with time and/or space for the same wave. Not constant. Light can have many wavelengths. If you’re talking visible light, different wavelengths produce different colours.