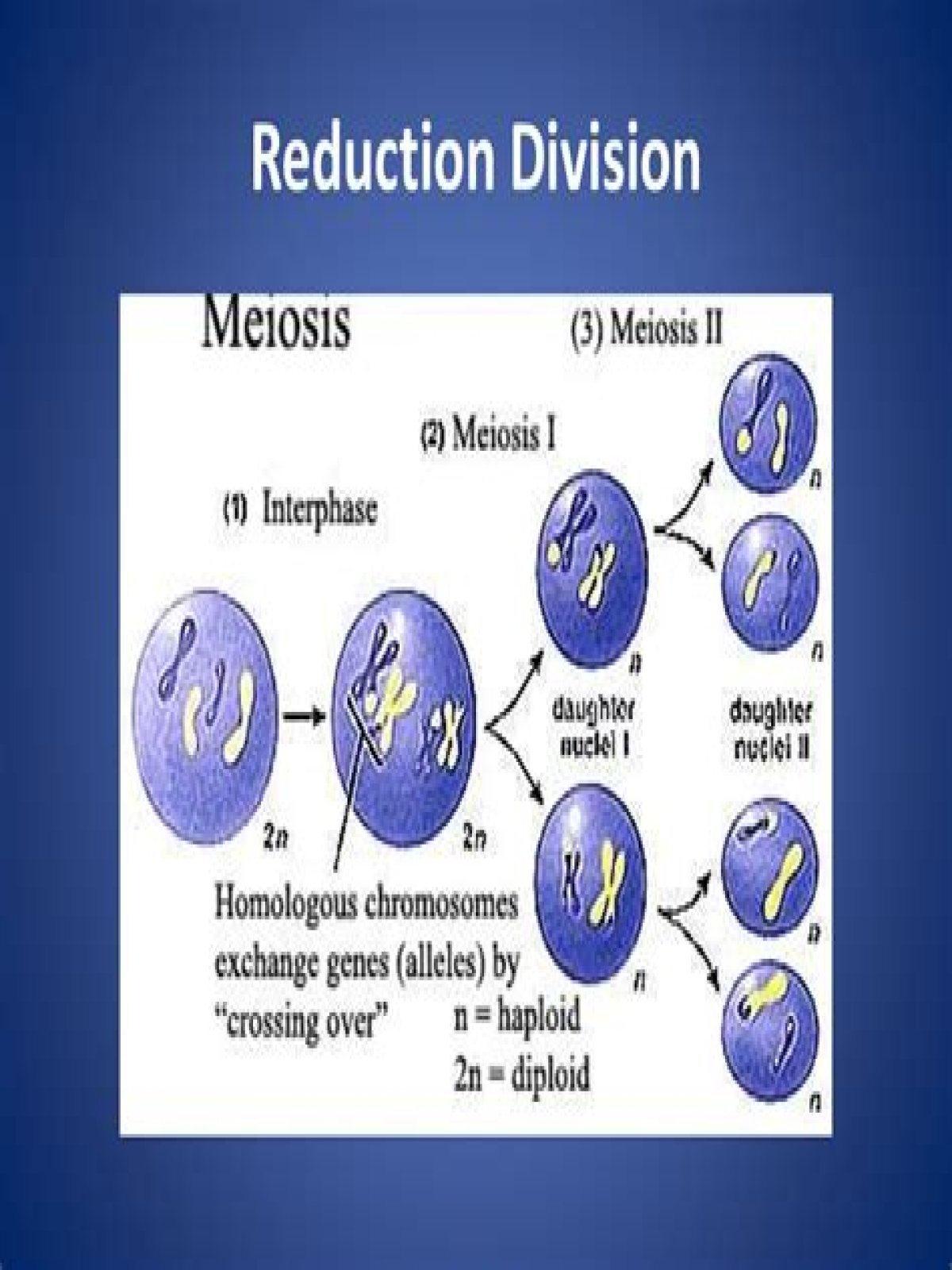
Which event makes meiosis a reduction division and why? separation of homologs in meiosis I because it produces 2 haploid (n) daughter cells from a single diploid (2n) parent cell. Separation of homologs results in a reduction in chromosome number.
- Why meiosis is a Reductional division?
- Which stage of meiosis is Reductional?
- Why is meiosis a Heterotypic division?
- How is meiosis a double division?
- Why is meiosis called Reductional division and mitosis called equational division?
- What is Reductional division and equational division?
- What does a bivalent consists of?
- Which is a Heterotypic division?
- What happens in Reductional division?
- What is Reductional division quizlet?
- Which is known as actual Reductional phase?
- Which events occur twice during meiosis?
- What events occur during meiosis I and meiosis II?
- What events occur during each phase of meiosis?
- Is mitosis Reductional or equational division?
- Is meiosis reduction division or equational division?
- Which cell division is known as equational division?
- Which is the Reductional division?
- What is the difference between homotypic and Heterotypic division?
- What is the meaning of Heterotypic?
- What happens Interkinesis?
- What does a bivalent of meiosis 1 consists of?
- What are bivalents and where are they found in the process of meiosis?
- What is bivalent chromosome and its effect in meiosis?
- Why meiosis is called reduction division Brainly?
- What process involves two divisions?
- In which stage of meiosis do homologous chromosomes or homologs separate?
- Which event leads to a diploid cell in a life cycle?
- What events occur during mitosis and meiosis?
Why meiosis is a Reductional division?
Meiosis is sometimes called “reduction division” because it reduces the number of chromosomes to half the normal number so that, when fusion of sperm and egg occurs, baby will have the correct number.
Which stage of meiosis is Reductional?
Meiosis I is called a reductional division, because it reduces the number of chromosomes inherited by each of the daughter cells.
Why is meiosis a Heterotypic division?
In meiosis -I, the homologous chromosomes seperate from each other and go to two different daughter cells. This reduces the number of chromosome from diploid to haploid condition. That is why meiosis-I is called heterotypic division or reduction division.How is meiosis a double division?
Homologue pairs separate during a first round of cell division, called meiosis I. Sister chromatids separate during a second round, called meiosis II. Since cell division occurs twice during meiosis, one starting cell can produce four gametes (eggs or sperm).
Why is meiosis called Reductional division and mitosis called equational division?
Meiosis is called as reductional division because the chromosome number gets reduced to its half whereas mitosis is equational division because the chromosome number remains the same after division.
What is Reductional division and equational division?
The key difference between equational division and reduction division is that equational division refers to meiosis II, during which the chromosomal number remains equal as haploid. In contrast, reduction division refers to meiosis I, during which the chromosome number reduces to half from the diploid state.
What does a bivalent consists of?
A bivalent consist of four chromatids and two centromeres. Bivalent is a pair of homologous chromosome lying together in the zygotene stage of prophase I of first meiotic division.Which is a Heterotypic division?
The first meiosis division are known as heterotypic division.
Why is mitosis called equational division?Explanation: Mitosis is called equational division because each of the two daughter cells formed, get the same number of chromosomes as the parent.
Article first time published onWhat happens in Reductional division?
Reduction division: The first cell division in meiosis, the process by which germ cells are formed. In reduction division, the chromosome number is reduced from diploid (46 chromosomes) to haploid (23 chromosomes). Also known as first meiotic division and first meiosis.
What is Reductional division quizlet?
A process of reduction division in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes in a diploid cell.
Which is known as actual Reductional phase?
A : Anaphase-I is actual phase of reduction in number of chromosomes.
Which events occur twice during meiosis?
Answer: Since cell division occurs twice during meiosis, one starting cell can produce four gametes (eggs or sperm). In each round of division, cells go through four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
What events occur during meiosis I and meiosis II?
Homologous pairs of cells are present in meiosis I and separate into chromosomes before meiosis II. In meiosis II, these chromosomes are further separated into sister chromatids. Meiosis I includes crossing over or recombination of genetic material between chromosome pairs, while meiosis II does not.
What events occur during each phase of meiosis?
StageMajor EventsAnaphase ITwo chromosomes of each with two chromatids of each homologous pair separate and move toward opposite poles.Telophase IChromosomes arrives at the spindle polesCytokinesisCytoplasm divides to produce two cells, each having half the original number of chromosomes
Is mitosis Reductional or equational division?
Mitosis is a type of cell division where the chromosomes replicate and equally distributed into two identical daughter cells The number of chromosomes in each daughter cell are equal to that of the parent cell which is thus called diploid. Therefore, the mitosis is known as equational division.
Is meiosis reduction division or equational division?
Reduction divisionEquational divisionIt occurs in somatic cellsIt occurs in germ cellsNucleus divides only onceNucleus divides twice2 daughter cells are formed4 daughter cells are formedDaughter cells are diploidDaughter cells are haploid
Which cell division is known as equational division?
Mitosis is called equational division because mitosis is the process of cell division in which the chromosomes replicates and equally distribute into two daughter cells.
Which is the Reductional division?
Meiosis I, often referred to as reductional division , is the first division in meiosis that reduces the genetic material from diploid (two sets of chromosomes) to haploid (one set of chromosomes).
What is the difference between homotypic and Heterotypic division?
during meiosis the mother nucleus divides twice, i.e., heterotypic division is followed by homotypic division. The number of chromosomes is reduced to half in the heterotypic division whereas the homotypic division is mitotic one and here number of chromosomes remains same.
What is the meaning of Heterotypic?
: different in kind, arrangement, or form.
What happens Interkinesis?
During interkinesis, the single spindle of the first meiotic division disassembles and the microtubules reassemble into two new spindles for the second meiotic division. Interkinesis follows telophase I; however, many plants skip telophase I and interkinesis, going immediately into prophase II.
What does a bivalent of meiosis 1 consists of?
Four chromatids and two centromeres.
What are bivalents and where are they found in the process of meiosis?
Bivalents are a pair of homologous chromosomes, where each chromosome is composed of two chromatids, one chromosome is paternal and the other maternal. Before the process of meiosis starts replication occurs, and each individual chromosome grows a sister chromatid which is attached to it by centromere.
What is bivalent chromosome and its effect in meiosis?
Bivalents, each composed of two chromosomes (four chromatids) align at the metaphase plate. The orientation is random, with either parental homologue on a side. This means that there is a 50-50 chance for the daughter cells to get either the mother’s or father’s homologue for each chromosome.
Why meiosis is called reduction division Brainly?
Since the number of chromosomes in the daughter cells is half that of the parent cell, meiosis is known as reduction division. MEIOSIS: That after meiosis, the number of chromosomes in the cells (gametic cells) is halved or decreased if you want. … This is due to the lack of chromosomal content.
What process involves two divisions?
Comparing Meiosis and Mitosis: Meiosis and mitosis are both preceded by one round of DNA replication; however, meiosis includes two nuclear divisions. The four daughter cells resulting from meiosis are haploid and genetically distinct.
In which stage of meiosis do homologous chromosomes or homologs separate?
In anaphase I, the homologous chromosomes are separated.
Which event leads to a diploid cell in a life cycle?
Fertilization between the gametes forms a diploid zygote. The zygote will undergo many rounds of mitosis and give rise to a diploid multicellular plant called a sporophyte.
What events occur during mitosis and meiosis?
Both mitosis and meiosis entail four main events: 1) a reproductive signal, 2) replication of nuclear DNA, 3) segregation of the replicated nuclear DNA into new daughter nuclei, and 4) division of the cytoplasm, or cytokinesis to produce new daughter cells.