Biological membranes have three primary functions: (1) they keep toxic substances out of the cell; (2) they contain receptors and channels that allow specific molecules, such as ions, nutrients, wastes, and metabolic products, that mediate cellular and extracellular activities to pass between organelles and between the …
- What is the main role of membrane proteins quizlet?
- What are three function of proteins?
- What are 4 functions of proteins?
- What are the 2 roles of the membrane proteins?
- What do membrane carbohydrates do?
- What are the three functions of proteins in the cell membrane quizlet?
- What are the 5 main functions of proteins?
- What are the 7 functions of proteins?
- What are the roles of protein for cell transport?
- What is the main function of the cell membrane?
- Why are carbohydrates and proteins important to cell membrane function?
- Why is it important for the cell membrane to be fluid?
- What is the function of transport proteins embedded in the cell membrane?
- How do proteins associate with membranes?
- Which of the following is a function of membrane proteins Mcq?
- What functions do lipids carbohydrates and proteins have in the cell membrane?
What is the main role of membrane proteins quizlet?
MEMBRANE PROTEINS- Receptors for signal transduction: … -Elements of the cytoskeleton and the extracellular matrix may be anchored to membrane proteins, which help maintain cell shape and fix the location of certain membrane proteins. -Others play a role in cell movement or bind adjacent cells together.
What are three function of proteins?
catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Many hormones are protein in nature; hormones control growth and metabolic activities of the body. Enzymes are globular protein.
What are 4 functions of proteins?
- Growth and Maintenance. Share on Pinterest. …
- Causes Biochemical Reactions. …
- Acts as a Messenger. …
- Provides Structure. …
- Maintains Proper pH. …
- Balances Fluids. …
- Bolsters Immune Health. …
- Transports and Stores Nutrients.
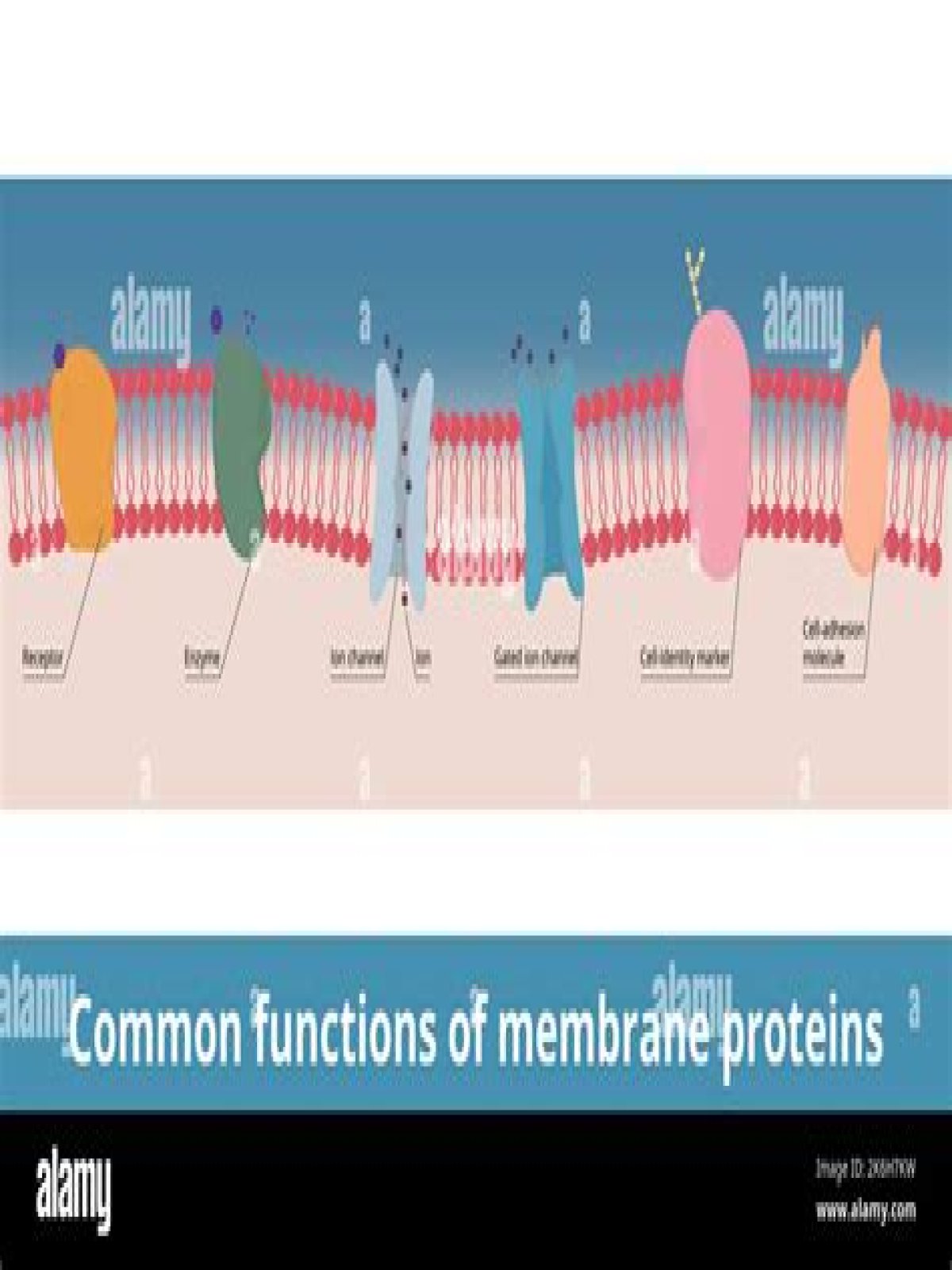
What are the 2 roles of the membrane proteins?
Membrane proteins perform a variety of functions vital to the survival of organisms: Membrane receptor proteins relay signals between the cell’s internal and external environments. Transport proteins move molecules and ions across the membrane. … Cell adhesion molecules allow cells to identify each other and interact.
What do membrane carbohydrates do?
Carbohydrates are made up of sugar molecules and can be joined to protein (glycoproteins and proteoglycans) or lipids (glycolipids). Carbohydrates protect the cell by forming a glycocalyx, which is especially strong in bacteria and enables biofilms to form.
What are the three functions of proteins in the cell membrane quizlet?
- Channels. allow specific ion’s to move through water filled pores.
- Transporters. they selectively move a polar substance or ions from one side of the membrane to the one.
- Receptors. are cellular recognition site they recognize and bind to a specific type of molecule.
- Enzymes. …
- Anchoring. …
- Identity.
What are the 5 main functions of proteins?
- Building Tissues and Muscles. Protein is necessary in building and repairing body tissues. …
- Hormone Production. Hormones are chemicals produced by glands in one part of the body that help coordinate activities and communicate with other areas. …
- Enzymes. …
- Immune Function. …
- Energy.
What are the 7 functions of proteins?
- Structure. Support for tissues. …
- Signaling. Chemical messengers. …
- Defense. Recognize and combine with other materials (Immunoglobins-antibodies of the immune system, cell membrane proteins)
- Transport. …
- Contractile. …
- Storage. …
- Enzyme.
- Repair and Maintenance. Protein is termed the building block of the body. …
- Energy. Protein is a major source of energy. …
- Hormones. Protein is involved in the creation of some hormones. …
- Enzymes. …
- Transportation and Storage of Molecules. …
- Antibodies.
What are the roles of protein for cell transport?
Functions of Transport Proteins Transport proteins function in both active and passive transport to move molecules across the plasma membrane. … These channel proteins are responsible for bringing in ions and other small molecules into the cell.
What is the main function of the cell membrane?
The plasma membrane, or the cell membrane, provides protection for a cell. It also provides a fixed environment inside the cell, and that membrane has several different functions. One is to transport nutrients into the cell and also to transport toxic substances out of the cell.
Why are carbohydrates and proteins important to cell membrane function?
Some of these proteins serve to transport materials into or out of the cell. Carbohydrates are attached to some of the proteins and lipids on the outward-facing surface of the membrane. These form complexes that function to identify the cell to other cells.
Why is it important for the cell membrane to be fluid?
Fluidity is important for many reasons: 1. it allows membrane proteins rapidly in the plane of bilayer. 2. It permits membrane lipids and proteins to diffuse from sites where they are inserted into bilayer after their synthesis.
What is the function of transport proteins embedded in the cell membrane?
Membrane transport proteins are specific and selective for the molecules they move, and they often use energy to catalyze passage. Also, these proteins transport some nutrients against the concentration gradient, which requires additional energy.
How do proteins associate with membranes?
Proteins can associate with the membrane in one of three ways. Intrinsic or integral membrane proteins embed in the hydrophobic region of the lipid bilayer. … Extrinsic or peripheral membrane proteins associate loosely with the hydrophilic surfaces of the lipid bilayer or intrinsic membrane proteins.
Which of the following is a function of membrane proteins Mcq?
Explanation: Transmembrane proteins act as channels from the intracellular and extracellular transport of ions and molecules. The channel through which the transport is done is called permeation pathway as it helps in the permeation of solutes and ions through the membrane.
What functions do lipids carbohydrates and proteins have in the cell membrane?
Carbohydrates covalently linked to proteins (glycoproteins) or lipids (glycolipids) are also a part of cell membranes, and function as adhesion and address loci for cells. The Fluid Mosaic Model describes membranes as a fluid lipid bilayer with floating proteins and carbohydrates.